AI Optimizes Bus Routes to Reduce Waiting Times
AI optimizes bus routes by forecasting demand, enhancing schedules, and minimizing delays—cutting passenger wait times and boosting transit efficiency.
Long waits at bus stops discourage riders and hurt transit's appeal. In many cities, waiting and transfer delays make up a large fraction of trip time – one study found off-vehicle waiting can account for roughly 17–40% of total journey time. Even small delays suppress ridership: in London a 1% increase in trip time led to about a 0.61% drop in transit use.
To tackle this, modern AI-driven scheduling tools analyze real-time and historical data (ridership patterns, traffic, weather, etc.) to generate smarter bus schedules and routes. These systems are designed to "create more accurate and reliable schedules" and promise "to reduce waiting times and improve on-time performance" for passengers.

AI Solutions for Public Bus Scheduling and Routing
AI supports transit planners in several ways to cut waiting times and delays:
Demand Forecasting
AI algorithms analyze past ridership, weather, events and time-of-day to predict when and where buses will be needed.
- Matches bus deployment to demand
- Prevents overcrowding and underutilization
- Optimizes vehicle deployment during peak times
Predictive Scheduling & Control
Machine learning learns which factors affect on-time performance and adjusts timetables accordingly.
- Analyzes traffic and boarding delays
- Provides real-time dispatch instructions
- Prevents delays and bunching before they happen
Transit-Signal Priority & Routing
AI integrates with traffic management to give buses priority at traffic lights or suggest alternate routes.
- Reduces red-light waiting by up to 80%
- Prevents bus bunching
- Optimizes route timing dynamically
Real-Time Passenger Information
Intelligent systems power digital displays and rider apps that predict bus arrival times.
- Accurate, up-to-the-minute schedules
- Makes waits feel shorter
- Improves customer experience significantly
One trial in Portland, OR using an AI traffic-priority system cut bus red-light waiting by roughly 80% over 15 miles, dramatically speeding up trips.
— Portland Transit Authority Research
These technologies work together to keep buses moving and passengers informed. For example, smart bus stops and apps now display AI-enhanced arrival forecasts so commuters know exactly how long they'll wait.
Real-World Examples of AI in Transit
Major transit operators are already reaping benefits. Here are some compelling case studies demonstrating the real-world impact of AI in public transportation:
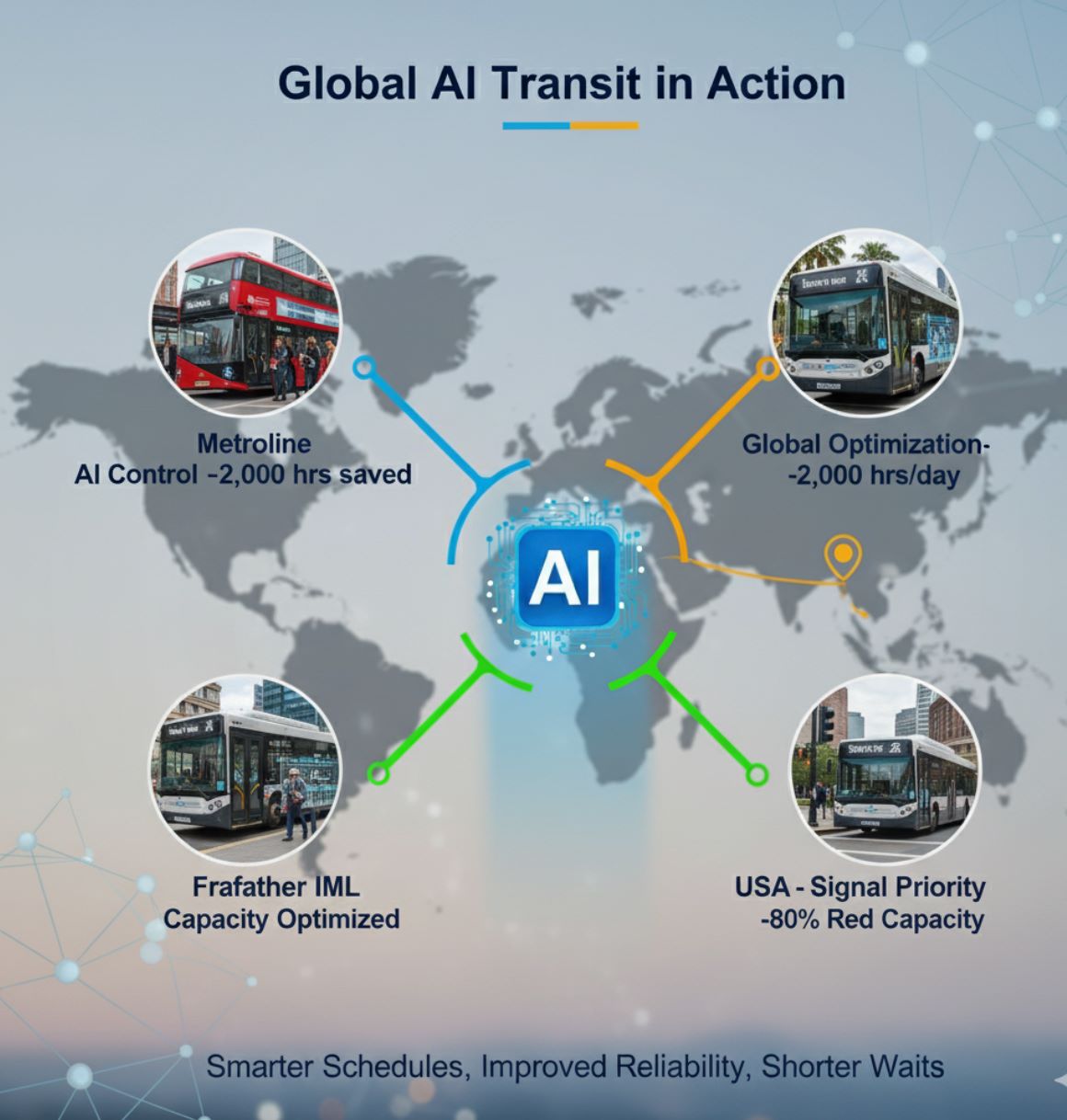
London - Metroline Success
Metroline piloted an AI-based control system (Prospective.io's FlowOS) to guide dispatchers and drivers.
- Significantly cut excess waiting time
- Saved passengers roughly 2,000 hours of collective wait time
- Now rolling out globally by ComfortDelGro
Singapore Expansion
Encouraged by London's success, ComfortDelGro is implementing the same AI system in Singapore.
- Trials project up to 2,000 passenger-hours saved per day
- Network-wide optimization
- Scalable AI deployment model
Germany - ÖPNV-Flexi Project
Germany's Fraunhofer IML tested AI-driven forecasts in Passau.
- Predicted passenger volumes accurately
- Adjusted fleet deployment dynamically
- Achieved better passenger distribution
- Reduced waiting times and optimized capacity
US Cities Implementation
Multiple US agencies are adopting AI-powered transit solutions.
- Boston and Seattle: AI-powered signal priority
- Ridership prediction and transfer coordination
- Reduced bus idling and delays
These cases illustrate the tangible impact of AI: smarter scheduling, improved reliability, and shorter waits. Transit agencies in many countries (from the US to Europe and Asia) are adopting these tools with measurable success.
Benefits and Future Outlook
AI-optimized transit offers multiple benefits that extend beyond simple time savings. By maintaining more consistent headways and reducing bunching, AI systems ensure buses arrive at regular intervals, so passengers don't face long unpredictable gaps.
Current Challenges
- Unpredictable waiting times
- Bus bunching and gaps
- Higher fuel and labor costs
- Poor passenger experience
AI Solutions
- Consistent, predictable schedules
- Dynamic scheduling prevents bunching
- 10% reduction in fuel costs
- Enhanced passenger comfort
Transit research shows that dynamic scheduling leads to shorter travel times and greater passenger comfort, while analyses suggest that a 10% drop in fuel use from better scheduling yields significant financial and environmental gains.
— Transit Research Institute
Operators also save money: fewer idle buses and smoother service mean lower fuel and labor costs, freeing resources for expanded service. In fact, analyses suggest that a 10% drop in fuel use (from better scheduling) yields significant financial and environmental gains.
Future Developments
Looking ahead, AI in transit will only grow. Advanced models can continuously learn from live data (GPS, passenger counts, etc.) to adapt to changing traffic and demand.
Smart City Integration
AI systems integrate with IoT sensors and 5G networks
Real-Time Optimization
Bus routes and signals constantly optimized in real time
Enhanced Service
More sustainable and attractive public transport

Future "smart city" systems may integrate AI with IoT sensors and 5G networks so that bus routes and signals are constantly optimized in real time. Early projects report that these digital technologies make public transport "more sustainable and attractive," especially in low-demand or complex networks.






No comments yet. Be the first to comment!