AI Applications in Smart City Development and Green Mobility
Artificial intelligence is playing a vital role in shaping smart cities and green mobility. From intelligent traffic management and digital twin infrastructure to electric vehicle optimization and energy-efficient transport systems, AI is enabling cities worldwide to reduce emissions, improve urban services, and achieve sustainable development goals.
Smart cities leverage data and technology to enhance urban life and sustainability. Innovations like the internet of things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) modernize city services and boost operational efficiency. By processing vast data streams from sensors, cameras, and city records, AI enables cities to anticipate challenges and respond proactively. For example, AI-driven models help planners reduce traffic congestion and greenhouse gas emissions. In essence, AI is central to creating greener, safer, and more connected urban environments.
Smart City Infrastructure
AI empowers urban infrastructure and planning through advanced digital systems. Cities now deploy digital twins and sensor networks to model buildings, roads, and utilities in real time. By integrating IoT, satellite data, and analytics, city governments detect patterns and forecast trends with precision.
Flood Resilience
Smart Energy
Predictive Planning
Key AI Infrastructure Initiatives
- Flood and disaster resilience: AI-driven models simulate weather and water flow, enabling proactive flood defenses and emergency response guidance.
- Smart energy management: AI coordinates distributed energy sources (solar, wind, EV charging) to stabilize the grid and reduce consumption.
- Predictive planning: AI analyzes traffic, pollution, and resource data to optimize investments, improve efficiency, reduce costs, and meet sustainability goals.

Green Mobility & Transportation
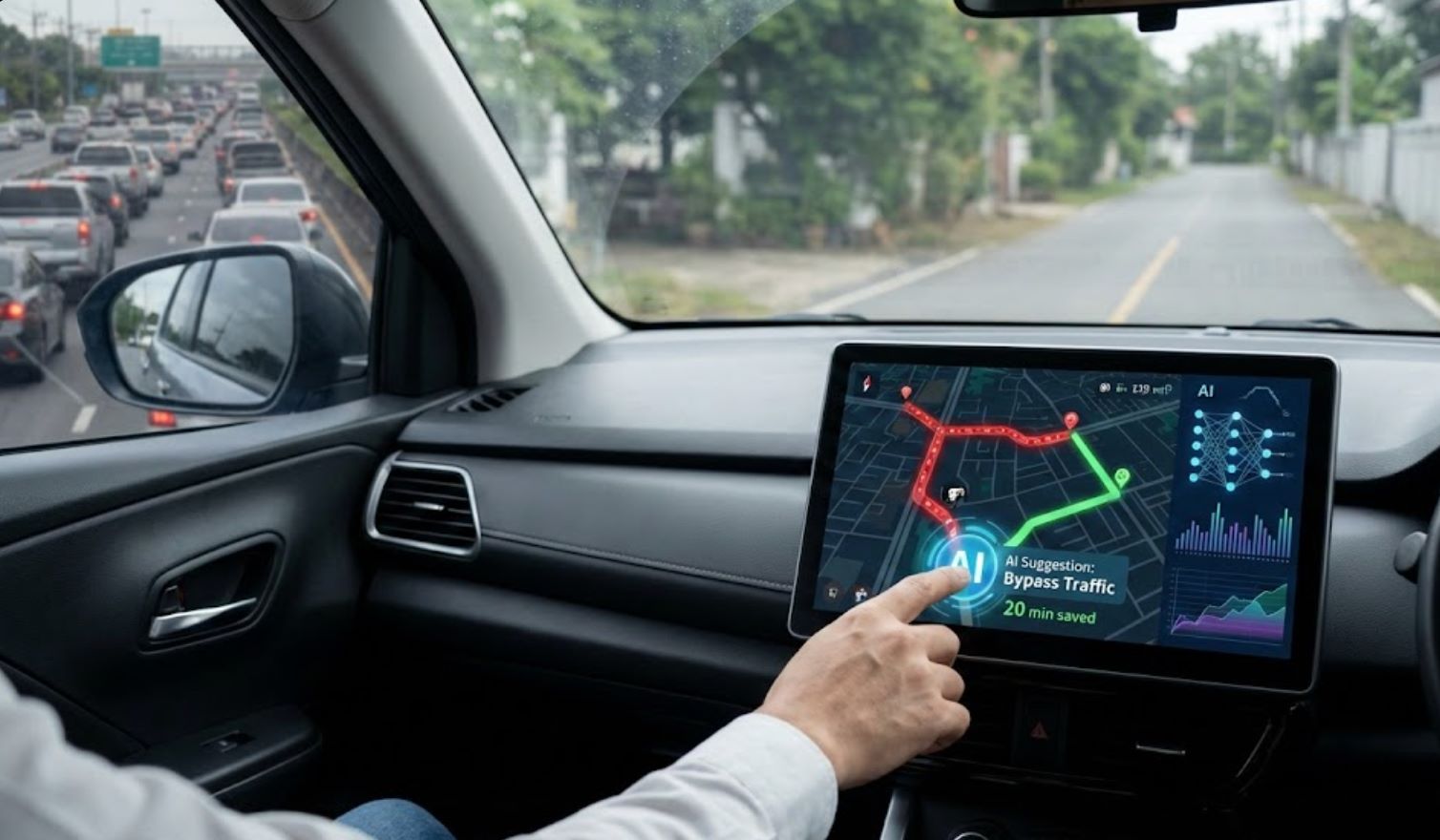
AI is transforming urban transportation to be cleaner and more efficient. Intelligent traffic systems use machine learning to reduce congestion and emissions significantly. Google's "Green Light" project demonstrates this impact: AI optimization of signal timing reduced traffic stops by ~30% and vehicle CO₂ emissions by ~10% at test intersections. The OECD confirms that "AI-enabled mobility can help cities reduce congestion, emissions and safety risks while improving accessibility."
Smart Traffic & Autonomous Systems
- Smart traffic signals: AI adjusts light cycles and coordinates intersections to smooth traffic flow and minimize idling.
- Autonomous transport: AI-driven vehicles (cars, buses, drones) continuously learn and adapt routes to avoid congestion in real time.
- Dynamic routing: Real-time analytics suggest alternate routes to drivers and riders, cutting travel times and fuel consumption.
Transit & Electric Vehicle Integration
Cities use machine learning to forecast ridership and optimize schedules. Transit agencies analyze historical and real-time data to deploy buses and trains where demand is highest, reducing wait times and preventing overcrowding. AI-driven predictive maintenance monitors vehicle sensors to flag issues before breakdowns occur, improving reliability and reducing downtime.
Demand Forecasting
AI predicts peak passenger loads and adjusts transit resources accordingly.
- Reduced wait times
- Optimized scheduling
- Better resource allocation
Predictive Maintenance
Machine learning identifies wear and faults early, enabling timely repairs.
- Fewer breakdowns
- Extended vehicle life
- Improved reliability
EV Charging Optimization
AI schedules charging during off-peak hours and aligns with renewable output.
- 97% prediction accuracy
- Grid stability
- Renewable integration

Challenges & Future Directions
While AI offers significant benefits, cities must address critical challenges to deploy it responsibly. Technology can inadvertently widen social gaps if not carefully managed. For example, Shenzhen's AI-based EV leasing program revealed stark disparities: only 12% of low-income households leased an EV compared to 62% of high-income households, due to entry barriers and accessibility issues.
Key Governance Priorities
Uncoordinated Systems
- Data silos and fragmentation
- Security vulnerabilities
- Lack of transparency
- Limited public engagement
Integrated Governance
- Robust governance frameworks and standards
- Open data and algorithm registries
- Cross-sector partnerships
- Public transparency and engagement
The OECD warns that uncoordinated AI systems (called "shadow AI") create silos and security risks. Cities need robust governance frameworks and standards to ensure services work together seamlessly. This requires transparency through open data initiatives and algorithm registries, plus meaningful public engagement to build trust in AI systems.
Path Forward
Cities worldwide continue piloting AI-smart solutions with growing sophistication. By balancing innovation with ethics and equity, urban planners aim for smarter, greener mobility and infrastructure. Success depends on:
- Clear policies and regulatory frameworks
- Cross-sector partnerships and collaboration
- Skills training and workforce development
- Inclusive design ensuring equitable access
- Transparent governance and public accountability

Conclusion
AI is rapidly reshaping urban development and transportation. Cutting-edge applications – from Lisbon's flood-predicting models to AI-managed EV grids and intelligent traffic lights – are already reducing energy use and emissions. As smart mobility systems scale globally, they promise safer streets, cleaner air, and improved transit experiences.
The key to successful smart city development is implementing AI with care: cities must build inclusive, transparent frameworks so that technological advances benefit all residents, not just the privileged few.
— Urban Planning & AI Governance Experts
With responsible planning and inclusive governance, the future city will be an AI-powered, green city – where data-driven decisions and low-carbon transport work together to enhance quality of life for everyone.






No comments yet. Be the first to comment!