AI analyzes CVs to assess skills
AI analyzes CVs to identify skills, providing faster, smarter, and more objective candidate assessments.
In today's competitive job market, AI-powered resume screening has become the norm. Understanding how these systems analyze CVs and assess skills is crucial for both job seekers and recruiters. This comprehensive guide explores the technology, benefits, challenges, and future of AI in recruitment.
- 1. AI's Dominance in Modern Recruitment
- 2. How AI Analyzes and Parses Resumes
- 3. Skills Assessment and Candidate Matching
- 4. Key Benefits of AI-Driven CV Analysis
- 5. Challenges, Bias, and Ethical Considerations
- 6. The Future of AI in Recruitment
- 7. Top AI Tools for CV Analysis
- 8. Conclusion: Balancing Power with Responsibility
AI's Dominance in Modern Recruitment
Artificial intelligence has fundamentally transformed how companies evaluate candidates. The numbers tell a compelling story about this technological shift in hiring practices.
Large Companies
Fortune 500
First Contact
These AI systems perform sophisticated analysis on each CV, scanning for key details including education credentials, work history, and most importantly, listed skills. They then compare these extracted data points against specific job requirements to determine candidate fit.
AI analyzes resumes at scale, identifying candidates who best match roles based on skills, experience, and other key factors.
— Industry Research Report on AI Recruitment
Behind the scenes, natural language processing (NLP) enables AI to go far beyond simple exact word matches. Modern systems understand context, recognize synonyms, and can interpret skills described in various ways across different resume formats.

How AI Analyzes and Parses Resumes
Modern AI resume parsing technology has evolved to handle diverse formats and extract meaningful data from unstructured documents. These sophisticated systems can even process photos of paper CVs, converting them into structured, analyzable data.
Document Ingestion
AI accepts resumes in multiple formats (PDF, Word, images, plain text) and uses optical character recognition (OCR) when needed to extract text from scanned documents or photos.
Section Identification
Machine learning algorithms identify and categorize different resume sections such as contact information, education, work experience, skills, certifications, and achievements.
Natural Language Processing
NLP technology analyzes the context and meaning of text, recognizing that "Java programming" and "software development" both indicate coding abilities, even when described differently.
Data Structuring
The system converts unstructured resume text into structured, searchable data fields that can be easily compared against job requirements and other candidate profiles.
Keyword Matching
- Simple exact word matches only
- Misses synonyms and variations
- Cannot understand context
- Struggles with diverse formats
Semantic Analysis
- Understands context and meaning
- Recognizes synonyms and related terms
- Handles multiple formats seamlessly
- Extracts nuanced skill information
Modern AI systems can scan resumes and prioritize applications using certain keywords while also applying semantic analysis to capture deeper meaning and context.
— Industry Guide on AI Recruitment Technology

Skills Assessment and Candidate Matching
After parsing each CV, AI systems perform sophisticated evaluation to determine how well a candidate's skills align with job requirements. This skills-based approach represents a fundamental shift in how companies identify qualified candidates.
The Skills Evaluation Process
Recruiters typically define a comprehensive skills profile for each role, specifying required technical abilities, soft skills, certifications, and experience levels. The AI then scores candidates based on how well they match these predefined criteria.
Technical Skills
Programming languages, software tools, technical certifications
- Exact skill matches
- Related technologies
- Proficiency indicators
Soft Skills
Leadership, communication, problem-solving abilities
- Context analysis
- Achievement indicators
- Role-based evidence
Experience Level
Years of experience, project complexity, career progression
- Duration analysis
- Project scope evaluation
- Responsibility growth
Proficiency Estimation
Advanced AI systems go beyond simply identifying whether a skill is present. They estimate proficiency levels by analyzing multiple factors:
- Years of experience with specific technologies or in particular roles
- Project counts and complexity as proxies for hands-on expertise
- Certifications and formal training that validate skill levels
- Achievement descriptions that demonstrate practical application
- Career progression showing increasing responsibility and expertise
Candidate Ranking Methods
Skills Match Scoring
AI platforms calculate a match percentage based on how many required skills a candidate possesses. Candidates are ranked from highest to lowest match scores.
- Weighted scoring for critical vs. nice-to-have skills
- Proficiency level consideration
- Minimum threshold filtering
Similarity to Successful Hires
Systems compare candidates to profiles of past successful employees in similar roles, identifying patterns that correlate with job performance and retention.
- Historical performance data analysis
- Pattern recognition from top performers
- Predictive success modeling
Adjacent Skills Discovery
Advanced AI can identify candidates with "adjacent skills" — those whose resumes don't have the exact job title but match nearly all required competencies, revealing hidden talent pools.
- Transferable skills identification
- Non-traditional candidate discovery
- Internal mobility opportunities

Key Benefits of AI-Driven CV Analysis
AI-powered resume screening delivers transformative advantages for recruitment teams, from dramatic time savings to improved diversity outcomes. Real-world implementations demonstrate measurable impact across multiple dimensions.
Massive Time Savings and Scale
AirAsia Case Study
Tech Conference Demo
This exponential increase in processing capacity means hiring teams can evaluate far more applications than ever before, ensuring qualified candidates don't slip through due to volume constraints.
Enhanced Diversity and Inclusion
When properly implemented, AI-based sourcing can significantly improve diversity outcomes by focusing on skills rather than traditional background indicators that may introduce unconscious bias.
Hidden Talent Discovery
AI excels at identifying qualified candidates who might be overlooked by traditional screening methods. By focusing on actual competencies rather than job titles or educational pedigree, these systems reveal valuable talent pools.
- Adjacent skills matching — Finding candidates whose experience translates well even without exact title matches
- Internal mobility opportunities — Identifying existing employees with transferable skills for new roles
- Non-traditional backgrounds — Surfacing self-taught professionals or career changers with relevant capabilities
- Overlooked applications — Rescuing strong candidates buried in high-volume applicant pools
Strategic Workforce Planning
Beyond immediate hiring needs, AI analysis of CV data provides valuable insights for long-term talent strategy and organizational development.
Skills Gap Analysis
Identify current workforce capabilities versus future needs
Predictive Analytics
Forecast looming skill shortages and hiring demands
Training Recommendations
Suggest development paths to close capability gaps
AI not only speeds up hiring but makes it more strategic by linking CV data to long-term talent goals, enabling proactive workforce development and succession planning.
— Workforce Analytics Research

Challenges, Bias, and Ethical Considerations
While AI offers powerful capabilities for resume screening, it also introduces significant risks that require careful management. Unchecked algorithms can perpetuate or even amplify existing biases, leading to unfair outcomes and potential legal liability.
The Bias Problem
AI systems learn from historical data, which means any bias present in past hiring decisions can be encoded and magnified in the algorithm. This creates a dangerous feedback loop where discriminatory patterns become automated and scaled.
Real-World Bias Examples
Amazon's Failed AI Recruiter
NLP Algorithm Bias
Regulatory Response
Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are recognizing the risks of biased AI in hiring and implementing oversight frameworks to protect candidates.
EU AI Act
The European Union is moving to classify AI hiring tools as "high-risk" systems, forcing vendors to ensure their data and algorithms are fair, transparent, and auditable.
- Mandatory bias testing and documentation
- Transparency requirements for decision-making logic
- Human oversight and appeal mechanisms
- Significant penalties for non-compliance
U.S. Local Regulations
Cities like New York are enacting specific rules requiring companies to audit AI hiring systems for bias before deployment and annually thereafter.
- Independent bias audits required
- Public disclosure of audit results
- Candidate notification of AI usage
- Alternative evaluation processes available
Industry Best Practices
Leading organizations are implementing comprehensive fairness frameworks that go beyond regulatory minimums.
- Regular algorithmic bias testing across protected categories
- Diverse training data that represents target candidate populations
- Human-in-the-loop decision making for final selections
- Continuous monitoring of hiring outcomes by demographic group
- Transparent communication with candidates about AI usage
The Essential Role of Human Oversight
Experts universally emphasize that AI should augment, not replace, human judgment in hiring decisions. Effective implementation requires a balanced approach.
Fully Automated Decisions
- AI makes final hiring decisions
- No human review of rejections
- Bias goes undetected
- No accountability or appeals
Human-AI Collaboration
- AI screens and ranks candidates
- Humans make final decisions
- Regular bias audits conducted
- Transparent appeal processes

The Future of AI in Recruitment
AI's role in hiring continues to expand beyond resume screening into strategic workforce planning, talent development, and organizational capability building. Emerging technologies promise even more sophisticated approaches to matching people with opportunities.
Generative AI Applications
The latest generation of AI tools leverages generative models to create and optimize recruitment content, moving beyond analysis into active content generation.
Job Description Generation
Auto-generate data-driven job descriptions that accurately reflect needed skills based on successful role profiles
Candidate Communication
Personalized outreach messages and interview scheduling that adapts to candidate preferences and context
Interview Question Design
Generate role-specific interview questions that assess critical competencies identified in CV analysis
Internal Mobility and Development
Forward-thinking organizations are applying AI CV analysis to their existing workforce, identifying internal talent and development opportunities that might otherwise remain hidden.
- Skills gap identification — Analyzing employee CVs and profiles to spot capability gaps for specific roles or future needs
- Training path recommendations — Suggesting personalized learning and development programs to close identified gaps
- Internal candidate matching — Finding existing employees whose skills align with new openings before external recruiting
- Succession planning — Identifying potential successors for critical roles based on skill proximity and development trajectory
Predictive Workforce Analytics
The next frontier combines CV analysis with broader workforce data to enable predictive planning and strategic decision-making about talent.
Demand Forecasting
Emerging Skills Detection
Workforce Optimization
Skills-First Hiring Model
AI will continue pushing the recruitment industry toward a comprehensive skills-first approach that fundamentally changes how we think about qualifications and career paths.
AI will continue pushing hiring toward a skills-first model, using CV data not just for filtering but for strategic workforce planning and candidate development, ultimately creating more equitable and effective talent systems.
— Future of Work Research Institute

Top AI Tools for CV Analysis
CV Sifter
Application Information
| Author / Developer | Smart Sifty (AI CV Sifter product) |
| Supported Devices | Web browser (desktop and mobile) — cloud-based platform via browser access |
| Languages / Countries | Global recruitment market; primarily English interface |
| Pricing Model | Paid service per CV processed / credit-based model (no free plan available) |
What is CV Sifter?
CV Sifter (also known as AI CV Sifter) is an AI-powered resume screening tool from Smart Sifty that automates candidate evaluation at scale. It reads, scores, and ranks CVs against job specifications, generating qualified shortlists within seconds. The platform reduces manual screening effort, improves hiring objectivity, and minimizes unconscious bias through algorithmic scoring and comprehensive fairness monitoring.
How CV Sifter Transforms Recruitment
Manual CV screening consumes significant recruiter time and often leads to inconsistent evaluations or overlooked qualified candidates due to high application volumes. CV Sifter automates this process by deploying AI models that parse resumes, extract critical attributes (experience, skills, education, certifications), and assign objective scores aligned with job requirements.
The system evaluates fairness across 20 bias dimensions including CV length bias, education bias, name complexity bias, and more. Recruiters simply input job requirements and upload CV batches — CV Sifter delivers ranked candidate lists with detailed scoring breakdowns. The tool integrates seamlessly into existing workflows, ensuring early-stage hiring decisions are data-driven, consistent, and fully auditable.

Key Features
Upload multiple resumes simultaneously and receive rapid candidate scoring with intelligent ranking based on job fit.
Adjust how different criteria (experience, skills, education) contribute to final candidate scores to match your hiring priorities.
Evaluates 20 types of bias including CV length, name complexity, and education bias to ensure regulatory compliance and fair hiring practices.
Integrates directly into existing recruiter workflows and ATS systems for streamlined candidate management.
Provides detailed explanations across multiple dimensions (experience, skills, education, cultural fit) for complete evaluation transparency.
Download or Access Link
How to Use CV Sifter
Create an account and log in to AI CV Sifter through the Smart Sifty portal to begin your automated screening process.
Specify the target role's attributes including required skills, education level, experience requirements, and other key qualifications.
Submit batches of candidate resumes to the system for automated processing and evaluation.
The AI processes each CV, scoring candidates across multiple dimensions (experience, skills, education, cultural fit) and generates a ranked shortlist automatically.
Examine detailed scoring for each candidate, including category-specific scores and overall ranking to understand evaluation rationale.
Choose the highest-ranked candidates from your shortlist for interviews or further assessment stages.
Fine-tune scoring weightings for different criteria or apply additional fairness controls to align with your specific hiring needs.
Important Limitations
- No free plan available — pricing is credit-based per CV processed
- CV format dependency — highly non-standard or creative resume formats may reduce parsing accuracy
- Human review still essential — AI predictions may struggle with niche, creative, or unconventional candidate profiles
- Integration complexity — connecting with older or custom ATS systems may require technical configuration
- Data quality matters — system performance depends on training data quality and ongoing bias management
Frequently Asked Questions
CV Sifter evaluates candidates across eight key areas: experience, education, hard skills, soft skills, languages, certifications, location & availability, and cultural fit. These dimensions are combined using a weighted formula to produce a final score out of 100, giving you a comprehensive view of each candidate's suitability.
Yes. The system actively monitors 20 types of bias and maintains regulatory compliance with GDPR, EEOC, UK Equality Act, and other relevant legislation through annual audits and continuous fairness monitoring.
Absolutely. The platform allows you to adjust the weightings of different scoring dimensions to align with your specific job priorities and organizational hiring criteria.
CV Sifter delivers rapid processing, generating scored and ranked results within seconds for batches of CVs, dramatically reducing time-to-shortlist compared to manual screening.
The platform is designed to integrate seamlessly into existing recruitment workflows, syncing with ATS systems and providing ranked shortlists as part of your early screening stage without disrupting established processes.
MyAiP CV
Application Information
| Author / Developer | FIVEN S.p.A. (MyAiP platform) |
| Supported Devices | Web browser (cloud) and on-premise deployment options |
| Languages / Countries | Global / international usage; primary interface in English, with presence in Italy and Europe |
| Pricing Model | Paid / enterprise model (demo or request access) — not publicly presented as free |
General Overview
MyAiP CV (also referred to as MyAiP CV Screener) is an AI-based resume screening solution, part of the MyAiP suite by FIVEN, designed to automate and accelerate the early stages of recruitment. It ingests large volumes of resumes, extracts relevant candidate information, ranks them by fit to role (hard and soft skills), and delivers a shortlist for recruiters. This reduces manual workload, improves consistency, and enables faster decision-making in recruitment.
Detailed Introduction
Recruiters often spend enormous time manually reviewing CVs, especially in high-volume hiring. MyAiP CV addresses this challenge by leveraging natural language processing (NLP), semantic analysis, and machine learning to read, decode, and interpret resumes in Word, PDF, or other formats.
It extracts candidate attributes (education, experience, skills, location, soft skills, etc.), generates both relative scores (comparing among candidates) and absolute scores (fit to role), and flags missing or conflicting information for manual review.
Its architecture supports integration with enterprise systems (e.g. Oracle, SAP, ADP, Workday) and allows deployment on cloud or on-premise, enabling HR teams to embed it into existing workflows.
MyAiP CV also attempts to automatically identify soft skills from textual cues — for example inferring leadership, communication, teamwork from experience, education, hobbies, and context.
In use cases (e.g. insurance, tourism), MyAiP enables bulk analysis, filtering by criteria (distance, years of experience), and then ranking and contacting shortlisted candidates.

Key Features
Process and rank hundreds of resumes within seconds, dramatically reducing screening time.
Extract hard and soft skills using semantic analysis and NLP methods for comprehensive candidate evaluation.
Relative scoring compares candidates against each other, while absolute scoring measures fit to role requirements.
Seamlessly integrates with HR/ATS systems like Oracle, SAP, ADP, and Workday with cloud and on-premise deployment options.
Automatically flags missing or conflicting information for manual validation or candidate follow-up.
Download or Access Link
User Guide
Visit the MyAiP website and request a demo or access to the platform.
Set up your search criteria, including required skills, experience level, location preferences, and other job-specific requirements.
Upload a batch of resumes in supported formats (Word, PDF) for automated processing.
MyAiP CV reads the documents, extracts salient information, infers soft skills, and handles conflicting data automatically.
Examine relative and absolute scores, review candidate rankings, and analyze the AI-generated insights.
Review top candidates, request missing details if needed, and contact qualified applicants for next steps.
Export shortlisted CVs, integrate results into your ATS, and continue with your recruitment process.
Important Notes & Limitations
- Accuracy depends on the quality and formatting consistency of submitted CVs — very nonstandard or creative CVs may reduce extraction performance.
- Automated inference of soft skills may not always capture nuanced or domain-specific traits.
- Integration into legacy HR systems may require custom adaptation or technical support.
- As with any AI tool, manual oversight remains essential to validate results and mitigate bias.
Frequently Asked Questions
MyAiP CV (or MyAiP CV Screener) is an AI-powered resume/CV screening tool that processes and ranks candidates based on their fit to job criteria.
Yes — MyAiP CV uses semantic analysis and natural language processing to infer soft skills from textual cues in experience, education, and other resume sections.
Yes — it supports integration with common enterprise and HR systems including Oracle, SAP, ADP, and Workday.
Processing is designed to handle bulk CVs in seconds or minutes, depending on volume.
No — MyAiP CV supports both cloud and on-premise deployments to align with business infrastructure needs.
SkillScore
Application Information
| Developer | SkillScore GmbH (operating via SkillScore.eu) |
| Platform | Web-based platform accessible via desktop and mobile browsers |
| Languages | English interface, targeting talent markets in Europe and worldwide |
| Pricing | Free basic features (profile creation, matching exploration); premium features available for recruiters and enhanced matching |
What is SkillScore?
SkillScore is an AI-driven talent matching and skill analytics platform that bridges the gap between candidates and recruiters. It helps professionals present their skills and experience in structured, machine-readable formats while enabling recruiters to discover talent through intelligent AI-based matching. The platform generates matching scores, optimizes resumes for applicant tracking systems (ATS), and enables filtered CV sharing—making recruiting smarter, faster, and more transparent.
How SkillScore Works
In a recruitment market flooded with resumes and generic job boards, SkillScore stands out with its data-centric matching engine. Candidates build comprehensive digital profiles—listing skills, projects, and experience—while the system automatically extracts and structures this information for optimal visibility.
For recruiters, SkillScore provides filtered candidate discovery, AI-powered ranking, and optimized resume export for ATS systems. This approach reduces noise, surfaces hidden talent, and helps both sides of recruitment efficiently find strong matches.
The platform supports advanced matching features including "Talent Matchmaker," "Hidden Champions," and "Career Compass," delivering insights on skill gaps, trending abilities, and role alignment to guide career and hiring decisions.
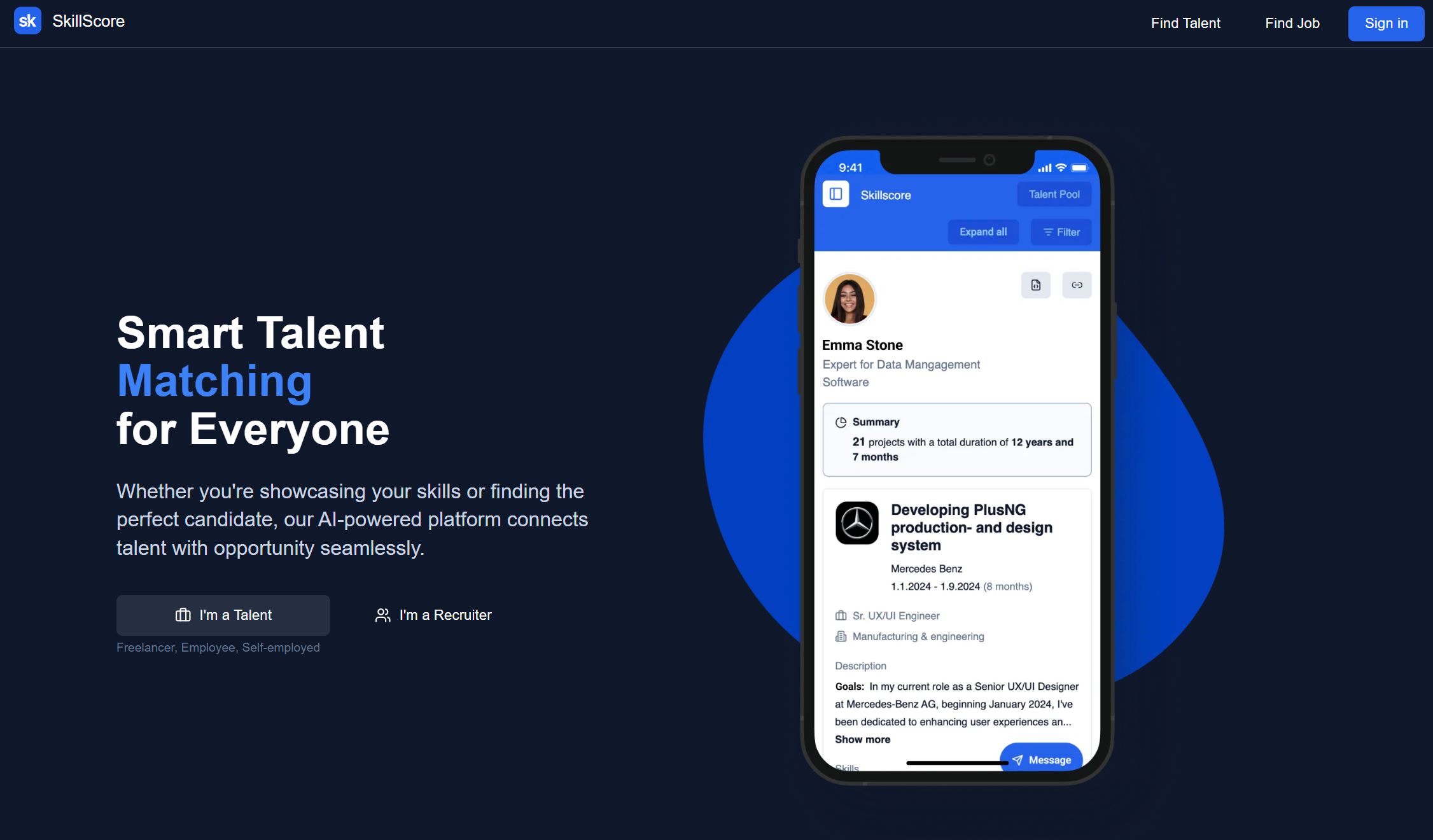
Key Features
Advanced profile matching and candidate ranking based on skills, experience, and role alignment using intelligent algorithms.
Create and export professional resumes optimized for applicant tracking systems in PDF, Word, or JSON formats.
AI extraction technology converts unstructured resume documents into structured, searchable skill data automatically.
Tailor which skills and sections to share with specific recruiters or roles for targeted applications.
Comprehensive recruiter tools including advanced search, intelligent matching, and analytics dashboards.
Download or Access Link
How to Use SkillScore
Register at SkillScore.eu and build your digital profile by adding skills, projects, certifications, and complete work history.
Use the AI extraction tool to automatically convert your existing resume into structured skill data, saving time on manual entry.
Review and adjust your skill tags, certifications, and experiences. Export your resume in ATS-friendly formats for maximum compatibility.
Use filtered CV sharing to send targeted versions of your profile to specific recruiters or companies, highlighting relevant skills.
Recruiters can search with advanced filters, view AI-ranked candidates, match them against job requirements, and contact selected talent.
Regularly update your skills and projects to maintain high visibility and relevance in AI matching algorithms.
Important Limitations
- Advanced features such as full recruiter analytics and access to large talent pools may require paid subscription tiers
- Matching algorithm quality depends heavily on profile completeness and accuracy—incomplete data results in lower quality matches
- AI extraction may misinterpret or omit information from nonstandard resume formats or creative layouts
- Integration with external HR systems or customized ATS setups may require additional configuration work
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, basic features such as profile building and job matching are completely free. Premium recruiter tools and advanced analytics may require payment.
SkillScore uses AI algorithms to score candidates based on over 100 factors including skills, experience, certifications, and role alignment. This produces a comprehensive matching score that recruiters can use to filter and rank candidates effectively.
Yes. SkillScore supports AI-powered extraction from PDF, Word, and other common formats to automatically convert your resume into structured, searchable data.
Recruiters can access basic candidate search features for free. Advanced tools, analytics dashboards, and premium features are typically part of paid subscription plans.
While SkillScore emphasizes tech and skills-driven roles, the platform supports a broad range of profiles and matching capabilities across multiple industries, including non-technical positions.
Conclusion: Balancing Power with Responsibility
AI-powered CV analysis represents a transformative shift in recruitment, offering unprecedented speed, scale, and the potential for more objective, skills-based hiring. The technology enables companies to process thousands of applications efficiently while often discovering qualified talent that traditional methods would miss.
The Promise
- Dramatic time and cost savings
- Ability to evaluate massive applicant pools
- Skills-focused, objective assessment
- Discovery of hidden talent
- Improved diversity outcomes
- Strategic workforce insights
The Responsibility
- Risk of encoded bias
- Need for transparency
- Regular fairness audits required
- Human oversight essential
- Regulatory compliance
- Ethical implementation practices
The most effective approach combines AI's efficiency with human judgment, ensuring technology amplifies opportunity rather than entrenches inequality. When implemented thoughtfully, AI can help create recruitment systems that are both more efficient and more equitable.
Incomplete Solution
- Risk of automated bias
- Lack of context understanding
- No accountability
Optimal Approach
- AI efficiency + human judgment
- Fairness monitoring + oversight
- Technology amplifying opportunity
Ultimately, AI's goal is to match candidates to jobs by genuine skills and potential, benefiting both employers and job seekers. When implemented with proper safeguards and human oversight, it can create recruitment systems that are faster, fairer, and more focused on what truly matters: capability and fit.
— AI Ethics in Recruitment Report
As AI continues to evolve, the recruitment industry must remain vigilant about fairness while embracing the technology's potential to create more skills-based, inclusive hiring practices. The future of work depends on getting this balance right.






No comments yet. Be the first to comment!