Tips for Using AI to Summarize Long Documents
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming how we handle information, saving hours of reading and analysis with its fast and accurate summarization capabilities. This article shares practical tips for using AI to summarize long documents effectively — from chunking text and crafting smart prompts to choosing the right tools like ChatGPT, Claude, or Google Gemini — helping you create concise, natural, and easy-to-understand summaries.
Summarizing very long texts with AI can save time, but it requires some strategy. AI-based summarization generally falls into two types: extractive (picking out key sentences from the original) and abstractive (generating a concise paraphrase of the ideas). In practice, modern AI (like GPT or Claude) can do either or both. However, most models have input length limits, so you usually must break up a long document into parts and combine results. Below are best practices and tips for doing this effectively.
Split Documents into Chunks (Map/Reduce)
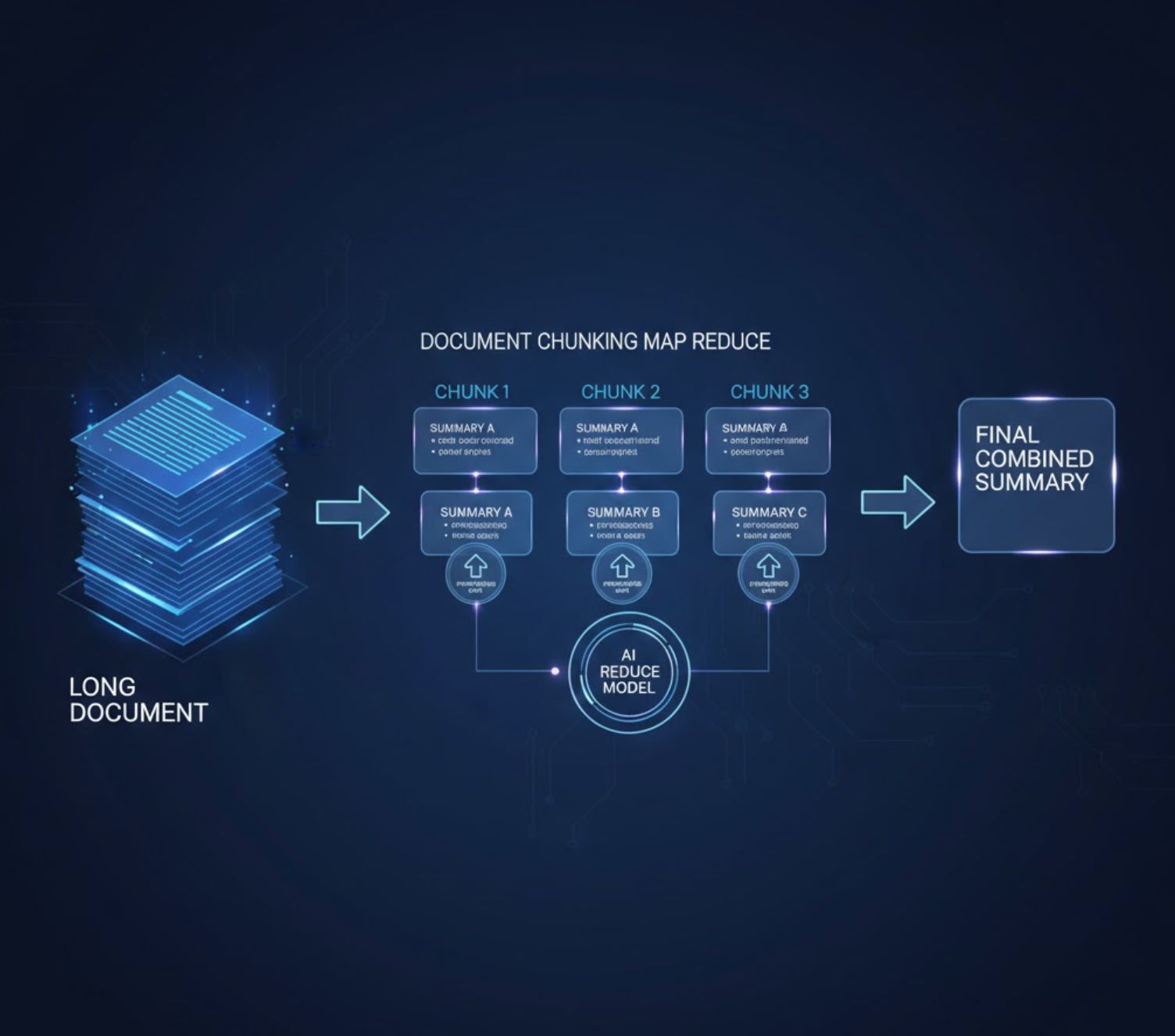
AI models have a finite context window, so you should divide a long document into manageable chunks (for example, by section, chapter, or logical segment) before summarizing. One effective strategy is the map/reduce approach:
Map/Reduce Strategy
Adjust Detail with Chunking
Iterative Refinement
Craft Clear Prompts
How you ask the model to summarize matters a lot. Good prompt design guides the AI to produce useful summaries. General guidelines include:
Include the Text to Summarize
Always provide (or upload) the actual content (or a portion of it) that you want summarized. The AI can only summarize what you give it.
Define the Task Explicitly
For example, start with "Summarize the following text: [your text]" or "Please generate a concise summary of the given article…". This makes clear that you want a summary, not some other transformation.
Provide Context or Role
Adding context can focus the summary. For instance, "You are given an article about Artificial Intelligence and its role in healthcare" helps the model know the topic.
Specify Format and Length
If you need bullet points, a paragraph, or a particular word count, say so. For example: "Write a summary in 5 bullet points, no more than 100 words: [text]". Setting a word or sentence limit prevents overly long answers.
Effective prompts might look like: "Summarize this [report/article/chapter] and list the key findings in 3–4 bullet points (max 150 words)." By clearly stating the goal and format, you help the AI produce concise, on-point summaries.

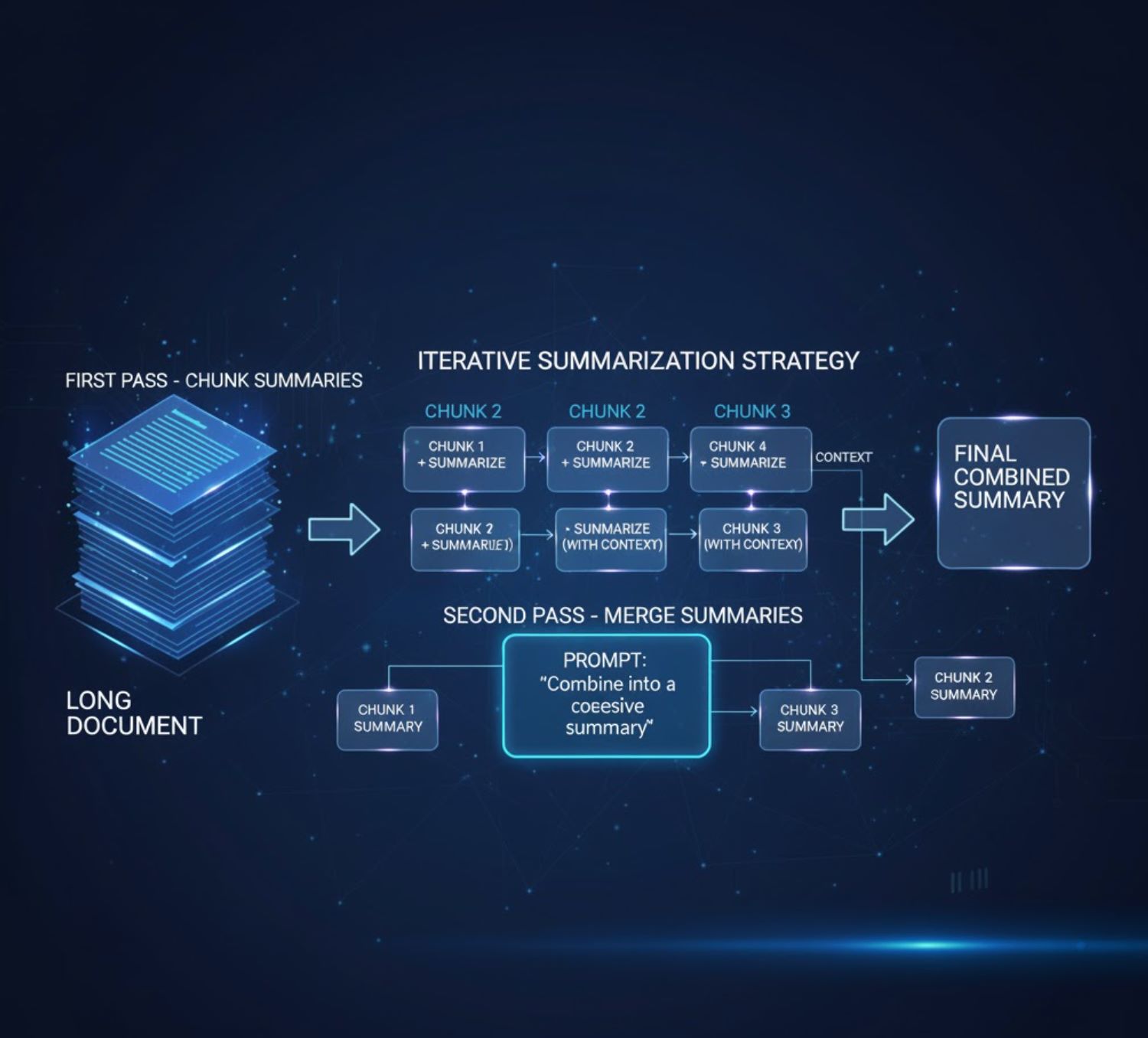
Use Iterative Summarization Strategies
For very long or complex documents, a two-stage or multi-stage approach often works best. One common method is:
Chunk Summaries
Summarize each section or chunk on its own. You can optionally feed the model a running summary of previous sections as context.
- Process each segment independently
- Maintain context from previous sections
- Example: "(For context, here is a summary of the first N segments: [summary so far]. Please now summarize the next segment…)"
Merge Summaries
After you have separate summaries of all chunks, ask the AI to consolidate them into one final summary.
- Combine all chunk summaries
- Create cohesive unified output
- Example: "Please combine the following bullet summaries into a single cohesive summary: [list of chunk summaries]"
This divide-then-combine strategy (sometimes called a hierarchical or recursive summary) ensures that no part of the document is overlooked. In practice, you might run your summarization loop like: summarize chunk 1, then chunk 2 (possibly with chunk 1's summary as input), and so on; finally, prompt the model to unify all chunk summaries.
Abstractive-Abstractive Pipeline
Map/reduce using LLMs: summarize each chunk with an LLM, then feed those summaries back into the LLM to produce a refined final summary.
Automated Workflows
Libraries like LangChain automate the "map" and "reduce" workflow, making implementation easier and more efficient.
Leverage the Right Models and Tools
Choosing a suitable AI model or tool is important. Many options exist:
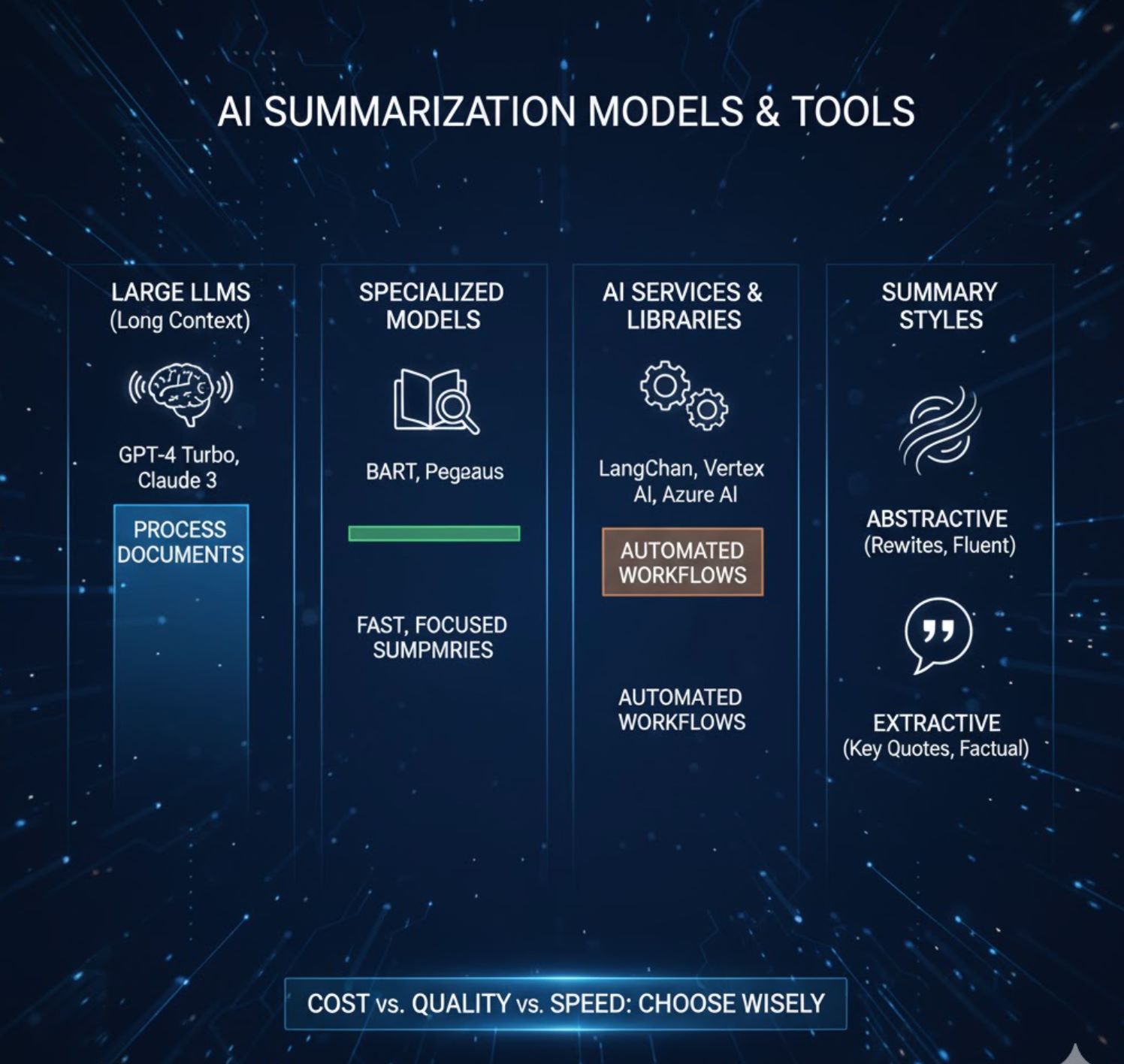
Large LLMs with Big Context Windows
Newer models can handle more input. For example, Anthropic's Claude 3 and OpenAI's GPT-4 Turbo support extremely long contexts (tens of thousands of tokens). If you have access to such models (via API or services like Amazon Bedrock, Google Vertex, or Azure OpenAI), they may require less manual chunking.
Claude 3
GPT-4 Turbo
Specialized Summarization Models
Models like Hugging Face's BART or Pegasus are fine-tuned for summarization. They often produce high-quality summaries on moderate-length text but have smaller token limits (typically ~1024 tokens). These can be a quick solution if your document is not excessively long.
BART
Pegasus
AI Services and Libraries
There are built-in summarization endpoints in some platforms. If coding, frameworks like LangChain offer summarization chains that implement map/reduce under the hood. Commercial tools might also have one-click summarizers.
- Google's Vertex AI - Summarization with PaLM/Gemini
- Azure AI - Dedicated summarization tools
- LangChain - Automated map/reduce chains
- Document AI products - One-click summarizers
Rewriting Content
- More flexible and fluent
- Paraphrases key ideas
- Best for narrative articles
Pulling Quotes
- Stays true to original wording
- Selects key sentences
- Best for technical reports
Review and Refine the Summary
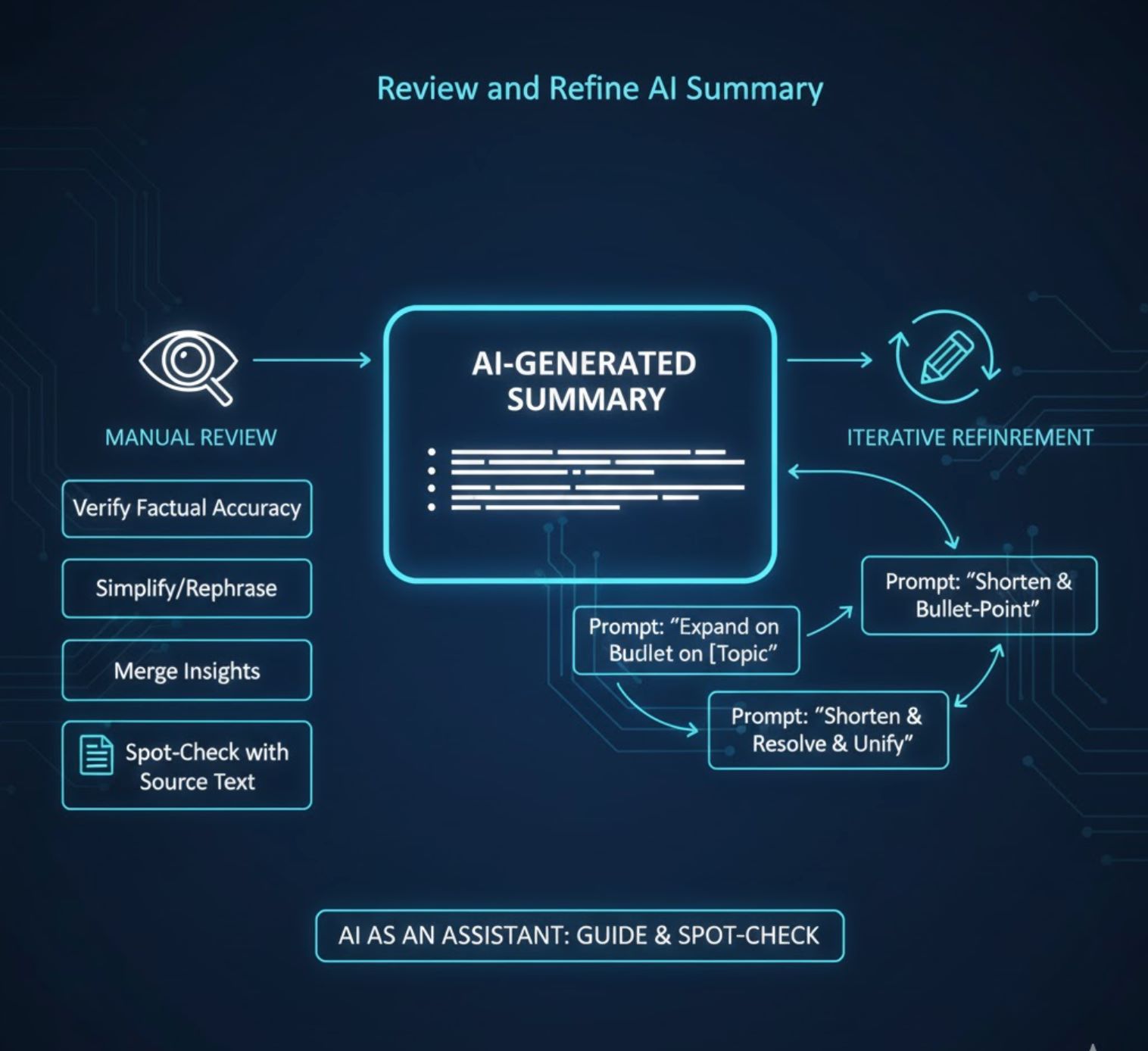
AI outputs aren't flawless. Always read over the AI-generated summary and check it against the source text. AIs can sometimes hallucinate details or miss nuances, especially in complex documents. You might need to:
Verify Factual Accuracy
Ensure all important points are included. If something's missing, you can prompt the model to "Expand on [that topic]" or re-run the summarization with a focus on the overlooked section.
Simplify or Rephrase
If the summary is too technical or verbose, you can instruct the model again to shorten or bullet-point the output further.
Merge Insights Manually
Sometimes the model's different chunk summaries overlap or contradict; a quick manual edit or a final prompt like "Please resolve these points into a clear, unified summary" can help.
Key Takeaways
Chunk Wisely
Break the document into parts that fit the model's input limit. Summarize each, then combine.
Ask Clearly
Your prompt should explicitly say "summarize" and include the text and any constraints (length, format).
Use Structured Workflows
Consider map/reduce or two-pass methods (summarize then merge) to handle very long text.
Pick the Right Tool
Use models with larger context (e.g. GPT-4 Turbo, Claude) or specialized summarizers (BART/Pegasus) as appropriate.
Refine Output
Review the AI's summary, fact-check it, and prompt again if needed to cover missing points.
By following these strategies—splitting the text, writing good prompts, and iteratively refining—you can get concise, accurate summaries of even very long documents using AI.







No comments yet. Be the first to comment!