What is Narrow AI and General AI?
What is Narrow AI and General AI? The core difference is that Narrow AI “knows everything about one thing, while General AI knows many things.” Narrow AI exists around us in specific applications, while General AI is the ambitious goal to create fully intelligent machines.
In today's technological era, artificial intelligence (AI) has permeated every aspect of life. We often hear about AI in everyday applications, from virtual assistants on phones to self-driving cars.
However, not all AI systems are the same. In fact, AI is classified into different levels, the most common being Narrow AI (Artificial Narrow Intelligence – ANI, also called Weak AI) and General AI (Artificial General Intelligence – AGI, also called Strong AI). So what exactly are Narrow AI and General AI, and how do they differ? Let's explore in detail with INVIAI below.
What is AI?
Before distinguishing Narrow AI and General AI, we need to understand what AI is. According to classic definitions by experts like Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig, AI is "the study and design of intelligent agents, where an intelligent agent is a system capable of perceiving its environment and taking actions to maximize its chances of success." Simply put, AI is the creation of machines or software that can perform tasks requiring human intelligence.
AI is the study and design of intelligent agents, where an intelligent agent is a system capable of perceiving its environment and taking actions to maximize its chances of success.
— Stuart Russell & Peter Norvig, AI Researchers
In reality, artificial intelligence includes many different systems, from simple algorithms to complex machine learning models. Based on scope and intelligence capability, AI is classified into Narrow AI (ANI), General AI (AGI), and even further into Superintelligent AI (ASI). Currently, Narrow AI is the only type that has been developed and widely applied, while General AI remains theoretical. To understand better, let's dive deeper into each concept.

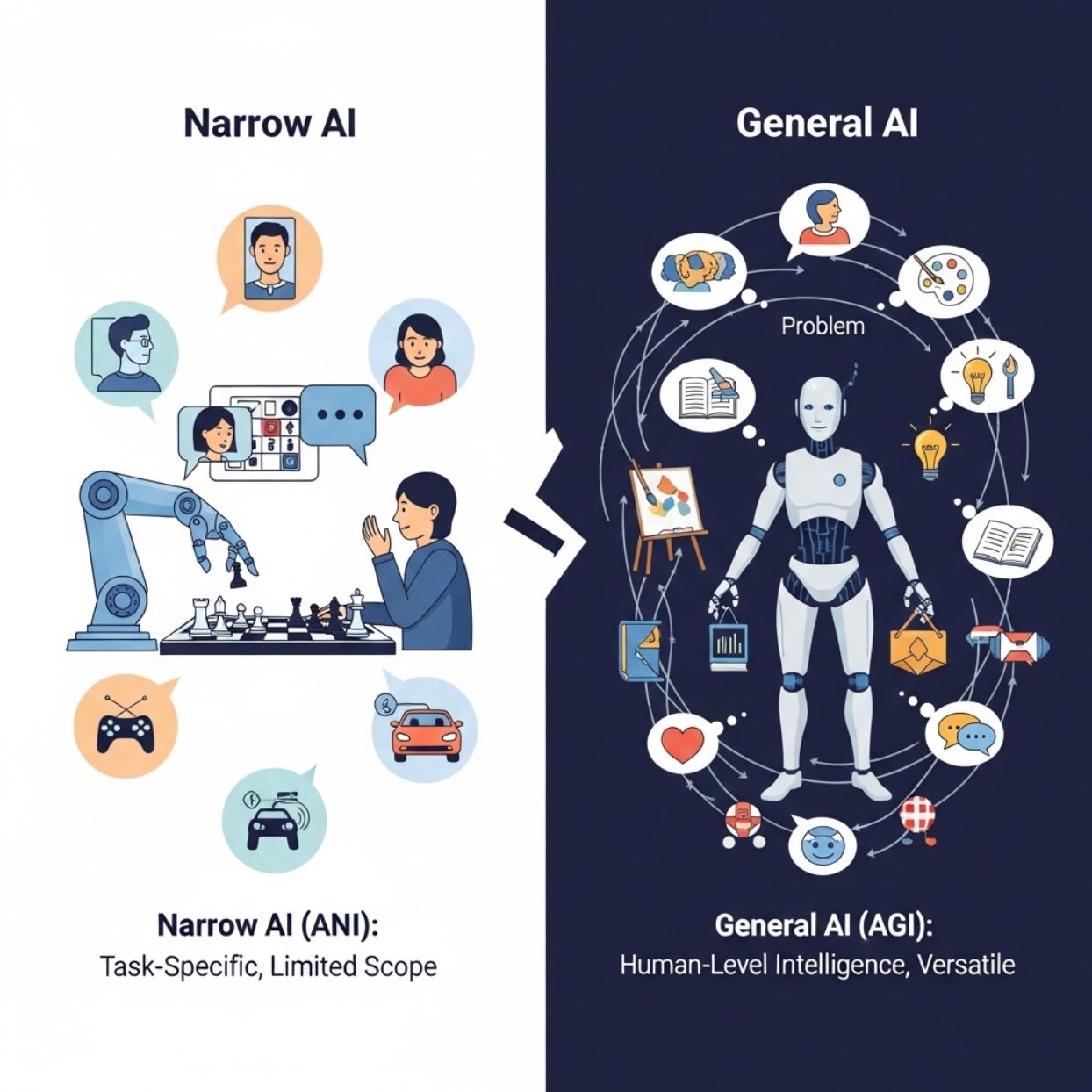
What is Narrow AI?
Narrow AI focuses only on a single domain or problem, such as facial recognition, language translation, playing chess, etc. Narrow AI excels within the scope of tasks it is programmed or trained for, and many systems even outperform humans in their narrow fields. However, Narrow AI lacks self-awareness or human-like reasoning and cannot extend its understanding beyond its programmed domain.
In other words, a Narrow AI system is like a super expert in one area but completely "blind" in others outside its specialty. This is why it is called Weak AI – not because it is weak in performance, but because its intelligence is limited within a predefined scope.
Common Examples of Narrow AI
Virtual Assistants
Recommendation Systems
Facial Recognition
Self-Driving Cars
Advantages and Limitations
Narrow AI Strengths
- High accuracy and outstanding performance in assigned tasks
- Practical benefits across industries (healthcare, finance, manufacturing)
- Reliable and consistent results within scope
- Cost-effective for specific applications
Narrow AI Constraints
- Restricted intelligence scope – cannot learn tasks outside training
- Zero flexibility beyond initial programming
- Fully dependent on provided data and algorithms
- Bias inheritance from training data errors
- No deep understanding – only pattern-based responses
Because of these limits, researchers have long aspired to develop a more advanced AI that can think broadly and flexibly like human intelligence – that is General AI (AGI).

What is General AI?
If Narrow AI is an expert in one field, then General AI is imagined as a "universal expert" capable of doing almost everything well – from driving, cooking, programming to medical diagnosis, legal advice, etc., similar to how an intelligent human can handle many different jobs.
Another way to imagine it: Strong AI is human-level artificial intelligence. It not only follows existing commands but can think independently, plan, create, and adapt when facing new situations – abilities Narrow AI lacks.
Independent Thinking
Can reason and make decisions without human guidance
Continuous Learning
Adapts and learns from new experiences across domains
Creative Problem-Solving
Generates novel solutions and approaches
In science fiction, General AI is often depicted as machines with human-like cognition and awareness, even emotions. For example, characters like J.A.R.V.I.S. in Iron Man or Samantha in Her are imagined AI with human-level intelligence. They can converse naturally, learn new knowledge, and flexibly handle countless human requests.
Although we have made remarkable progress in Narrow AI, General AI remains a major challenge and may take decades more research.
— Ethan Mollick, Associate Professor, University of Pennsylvania
Why is Creating General AI So Difficult?
The reason is that to have human-like intelligence, AI must integrate many complex abilities: from language understanding, image perception, logical reasoning, abstract thinking, to learning from experience and social adaptation. This requires breakthroughs in algorithms, massive computing power, and vast, diverse training data.
Technical Challenges
Requires breakthroughs in algorithms, massive computing power, and vast diverse training data
Safety Concerns
Ensuring AI behaves ethically and humans retain control over superintelligent systems
Social & Philosophical Issues
Addressing societal impact, governance, and philosophical questions about consciousness
Additionally, there are countless ethical and safety issues to consider when developing human-level AI – such as ensuring it behaves ethically and that humans retain control if it becomes too intelligent. This is not only a technological problem but also involves social and philosophical aspects.
Current Progress Toward AGI
Although true AGI does not yet exist, recently some advanced AI systems have begun to show some generalization ability. For example, large language models (e.g., OpenAI's GPT-3, GPT-4) can perform various tasks: answering questions, writing, programming, translating, even passing some human tests.
Still, even these advanced models are classified as Narrow AI by definition, because they lack true autonomous learning and remain constrained by technical and data limitations.
For example, a generative AI like ChatGPT has broad knowledge but cannot autonomously learn new knowledge beyond its initial training data, nor can it switch to physical tasks in the real world without further programming. Therefore, true General AI remains a future goal, not present reality.
Hypothetical Examples of Future General AI
Versatile Humanoid Assistant
All-Purpose AI Doctor
These examples do not yet exist but represent the vision AI researchers aim for. If one day we create successful General AI, it would be a giant leap in technology – potentially a new "industrial revolution" in human history.
However, alongside benefits come significant challenges and risks, as mentioned: how to control an intelligence capable of self-improvement beyond human understanding? This is why there is much debate around AGI development, requiring cautious progress.
If AGI is human-level intelligence, then ASI is superior intelligence. Some worry that if ASI emerges, it could cause unpredictable consequences for humanity because it would be too intelligent and beyond our control. However, that is a story for the distant future. In this article, we focus on two feasible and closer levels: Narrow AI (present) and General AI (near future/hopeful).

Differences between Narrow AI and General AI
In summary, Narrow AI (ANI) and General AI (AGI) differ fundamentally in many aspects. Below is a comparison and explanation of key differences between these two types of AI:
| Aspect | Narrow AI (ANI) | General AI (AGI) | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Task Scope | One or few specific tasks | Any intellectual task humans can do | Limited vs Universal |
| Flexibility | Cannot adapt beyond training | Learns and adapts to new situations | Rigid vs Adaptive |
| Current Status | Exists and widely used | Theoretical, not yet achieved | Present vs Future |
| Learning Ability | Depends on pre-programming | Self-directed learning and reasoning | Programmed vs Autonomous |
| Control Level | Safer and easier to control | Greater ethical and control risks | Manageable vs Complex |
Task Scope Comparison
Narrow AI can only perform one or a few specific tasks it has been programmed or trained for (e.g., only image recognition or only playing chess). In contrast, General AI aims to perform any intellectual task a human can do, meaning its scope is not limited to any domain.
Simply put, Narrow AI is a "grain of sand" while General AI is an "ocean" of capability.
Flexibility and Learning Capabilities
Narrow AI lacks the ability to learn and adapt to new situations beyond its initial data/algorithms – it depends entirely on pre-programming and provided data. Meanwhile, General AI is expected to adapt and learn new knowledge when facing unfamiliar problems, similar to how humans learn from experience.
General AI can reason, form consciousness, or at least have general understanding of the world, rather than just following preset patterns.
Examples and Development Status
Narrow AI exists and is widely used today (in applications, services, smart devices everywhere) – including virtual assistants (Siri, Alexa), automatic translation software, movie recommendation systems, game programs (chess, Go), etc.
General AI remains theoretical, with global labs researching but no system has achieved this level of intelligence. Currently has no real examples, existing only as imagined models in movies and novels.
Advantages & Limitations
Narrow AI has the advantage of high specialization, often achieving superior accuracy and performance in its tasks (e.g., AI diagnostic imaging can analyze thousands of X-rays faster and as accurately as doctors).
However, its limitations include lack of flexibility, creativity, and dependence on data, unable to expand capabilities.
General AI, if successful, would be extremely flexible, adaptive, and creative – its greatest strength. But its current drawback is that it is very difficult to develop and involves many technical and social challenges.
Generally Safer
- Easier to control and predict
- Limited scope reduces major risks
- Bias from poor training data
- Context misinterpretation within narrow scope
Greater Challenges
- Ethical and control complexity
- Self-improvement without human intervention
- Alignment with human values
- Unpredictable consequences if goals misalign
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between Narrow AI and General AI is the first step to grasp the big picture of artificial intelligence today and in the future. Narrow AI has brought countless practical benefits in life, from automating tasks, increasing labor productivity, to improving services and daily conveniences. We are familiar with Narrow AI applications like virtual assistants, self-driving cars, data analysis... Narrow AI is the foundation of the current AI era, effectively solving specific problems.
Meanwhile, General AI is like the holy grail in AI research – a distant but promising goal. If one day General AI is achieved, humanity could witness major transformations: machines capable of doing almost everything humans do, opening new possibilities in science, healthcare, education, economy...
However, alongside hope come significant challenges in both technology and ethics. The journey to AGI is still long and requires interdisciplinary collaboration among scientists, engineers, social experts, and governments.
Today's Reality: Narrow AI
Powerful within narrow scope, strongly supporting humans in specific tasks
- Widely implemented and proven
- High performance in specialized domains
- Practical business applications
Future Vision: General AI
All-purpose human-like intelligence, promising but challenging to achieve
- Universal problem-solving capability
- Human-level reasoning and creativity
- Requires breakthrough innovations
In summary, Narrow AI and General AI represent two different levels of artificial intelligence. Narrow AI is today's reality – powerful within a narrow scope, strongly supporting humans in many specific tasks. General AI is the future vision – an all-purpose human-like intelligence, promising but also challenging to achieve.
As emphasized: currently, we have only conquered Narrow AI, while the path to General AI (and beyond to Superintelligent AI) remains very long.
Nevertheless, every step forward in AI research brings us closer to that goal. With the rapid development of technology, who knows, in a few decades, what was once science fiction may gradually become reality.







No comments yet. Be the first to comment!