What is AI?
AI (Artificial Intelligence) is the capability of computer systems to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making.
- 1. Understanding Artificial Intelligence
- 2. What is AI? – Definition and Origin of the Term
- 3. Types of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 4. Core Technologies and How AI Works
- 5. Practical Applications of AI in Life
- 6. Benefits of AI for Life and Society
- 7. Challenges and Limitations of AI
- 8. The Future of AI – Trends and Prospects
- 9. Conclusion
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be simply understood as a technology that helps machines "think" and solve problems similarly to humans. AI stands for Artificial Intelligence – meaning intelligence created by humans. Today, AI is everywhere, quietly powering many familiar applications in our daily lives. From virtual assistants on phones, movie recommendations, to self-driving cars and robots – all involve AI.
What is AI? – Definition and Origin of the Term
AI (Artificial Intelligence) is the ability of computer systems to perform tasks that usually require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making.
— Core Definition of Artificial Intelligence
In other words, AI is a technology programmed for machines to simulate human thinking – able to recognize images, create poetry, make predictions based on data, and more. The ultimate goal of AI is to create "intelligent" software that can automate complex tasks and interact naturally with humans.
Learning
Machines acquire knowledge from data and experience
Reasoning
Logical analysis and problem-solving capabilities
Perception
Understanding and interpreting sensory information
Historical Development
The Turing Test
Computer scientist Alan Turing posed the famous question "Can machines think?" and proposed the Turing Test to evaluate machine intelligence.
Birth of AI
The term AI officially appeared when the field was established as an independent scientific discipline.
AI Renaissance
Strong resurgence thanks to the combination of big data, machine learning algorithms, and computing power using GPUs to accelerate deep learning algorithms.
Generative AI Boom
The emergence of advanced Generative AI models like ChatGPT sparked a new "AI boom," while also raising ethical concerns and the need for governance.
Types of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Narrow (Weak) AI vs. General (Strong) AI
Specialized Intelligence
- Designed for specific tasks
- Excels within limited scope
- Virtual assistants (Siri, Alexa)
- Self-driving cars
- Facial recognition software
Human-Level Intelligence
- Human-level versatile intelligence
- Self-learning capabilities
- Cross-domain problem solving
- Understanding and reasoning
- Any intellectual task humans can do
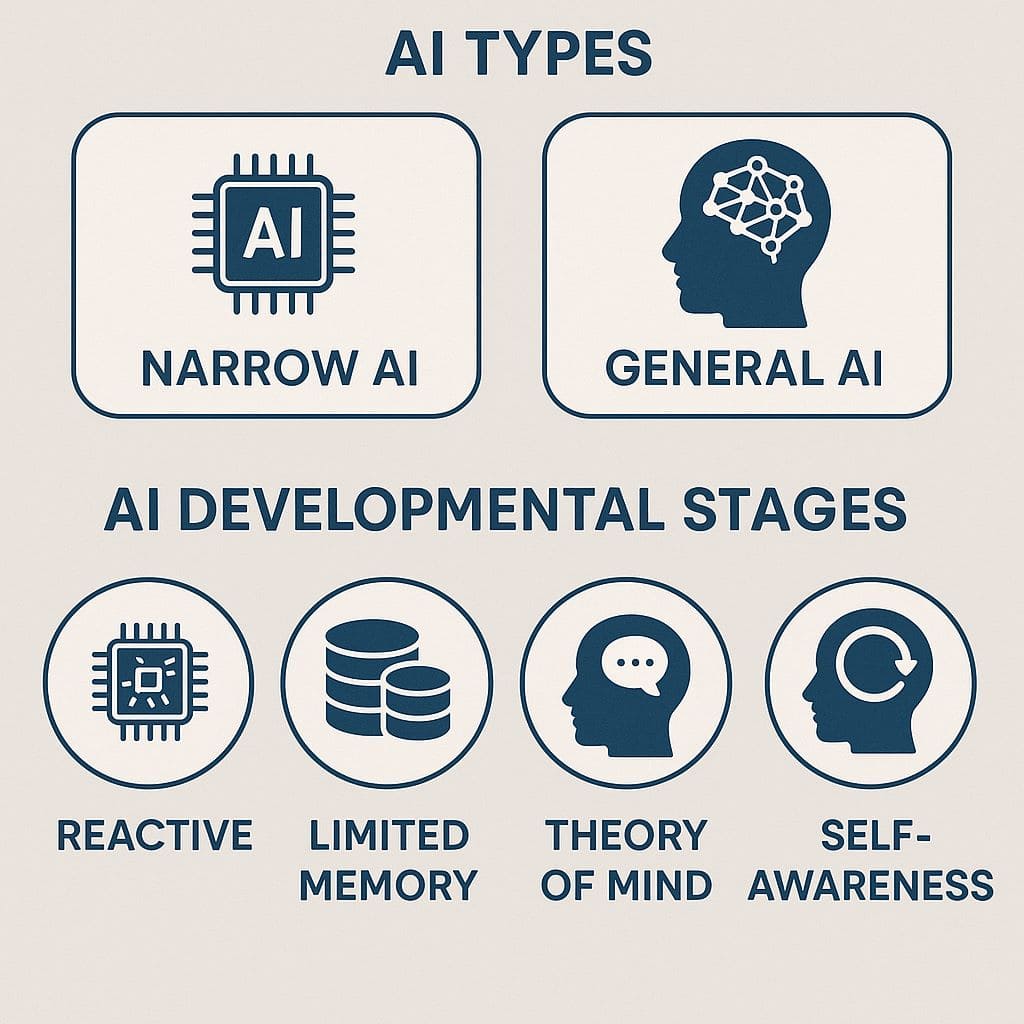
Four Levels of AI Development
Professor Arend Hintze (Michigan State University) proposed four evolutionary AI levels based on intelligence complexity and "thinking" ability:
Reactive Machines
This is the simplest form of AI, with no memory and only reacts to the present. These AI systems are programmed to handle specific tasks based on what they "see" at the moment, without learning from past experiences.
Example: IBM's Deep Blue
Limited Memory
At this level, AI has memory and uses past experiences to inform current decisions. Many AI systems today belong to this type.
Example: Self-Driving Cars
Theory of Mind
This is an AI level currently under research and not yet perfected. The "theory of mind" means AI can understand human emotions, intentions, and thoughts or those of other entities.
Self-Awareness
This is the highest and still hypothetical level. Self-aware AI is defined when machines have consciousness of themselves, understanding their own state as independent entities.
Overall, most AI today belongs to Types 1 and 2, meaning reactive or limited memory. Types 3 and 4 remain in the future. This classification helps us imagine the development roadmap of AI: from machines that only react, gradually advancing to those that can understand and be self-aware – the ultimate goal humans hope to achieve in artificial intelligence.
Core Technologies and How AI Works
When talking about AI, people often mention "machine learning" and "deep learning". In fact, machine learning is a crucial branch of AI. If AI's goal is to make machines intelligent, then machine learning is the method to achieve that goal – it includes techniques and algorithms that enable computers to learn from data rather than being explicitly programmed.
Artificial Intelligence
Machine Learning
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a specialized branch of machine learning that uses multi-layer artificial neural networks (inspired by the human brain) to learn complex features from data. The explosion of deep learning in the past decade has propelled AI to remarkable progress, as machines began to "learn from millions of examples", enabling tasks like image recognition and natural language understanding with high accuracy.
How AI Works
Input Data
AI requires input data (images, audio, text) as raw material for learning
Pattern Analysis
Algorithms analyze and extract rules or patterns from the data
Apply Knowledge
Apply learned rules to handle new situations and make predictions

Unlike traditional programming (writing fixed step-by-step instructions), AI programming focuses on creating models that can improve accuracy through experience.
Core Components of AI
Algorithms and Models
The "brain" of AI, determining how AI learns and makes decisions
- Neural networks
- Decision trees
- Genetic algorithms
Data
The "fuel" for AI - the more and higher quality the data, the better AI learns
- Sensor data
- Text and images
- User activities
Computing Power
Hardware advances enable training complex AI models in shorter times
- GPUs for acceleration
- TPUs for AI workloads
- Cloud computing
Human Expertise
Humans play a crucial role in designing, training, and supervising AI systems
- Algorithm design
- Data preparation
- Training supervision
Main AI Fields
The core of modern AI, enabling machines to learn from data and improve performance over time without explicit programming for each task.
Helps machines see and understand images/videos with applications ranging from facial recognition, medical image analysis to autonomous vehicles.
Helps machines understand and communicate in human language, used in machine translation, virtual assistants, chatbots, and sentiment analysis.
AI systems that make decisions based on sets of rules and domain knowledge, such as medical diagnosis based on symptoms.
Focuses on building intelligent robots that interact with the real environment and perform tasks on behalf of humans.
All these branches aim for the common goal: helping machines become "smarter" to assist humans in solving problems effectively.
Practical Applications of AI in Life
One simple way to understand what AI is is to look at what AI is doing in practice. Today, artificial intelligence is widely applied across almost all fields, from daily life to business production.
Search Engines
Recommendation Systems
Virtual Assistants
Self-Driving Cars
AI Content Creation
Game Intelligence
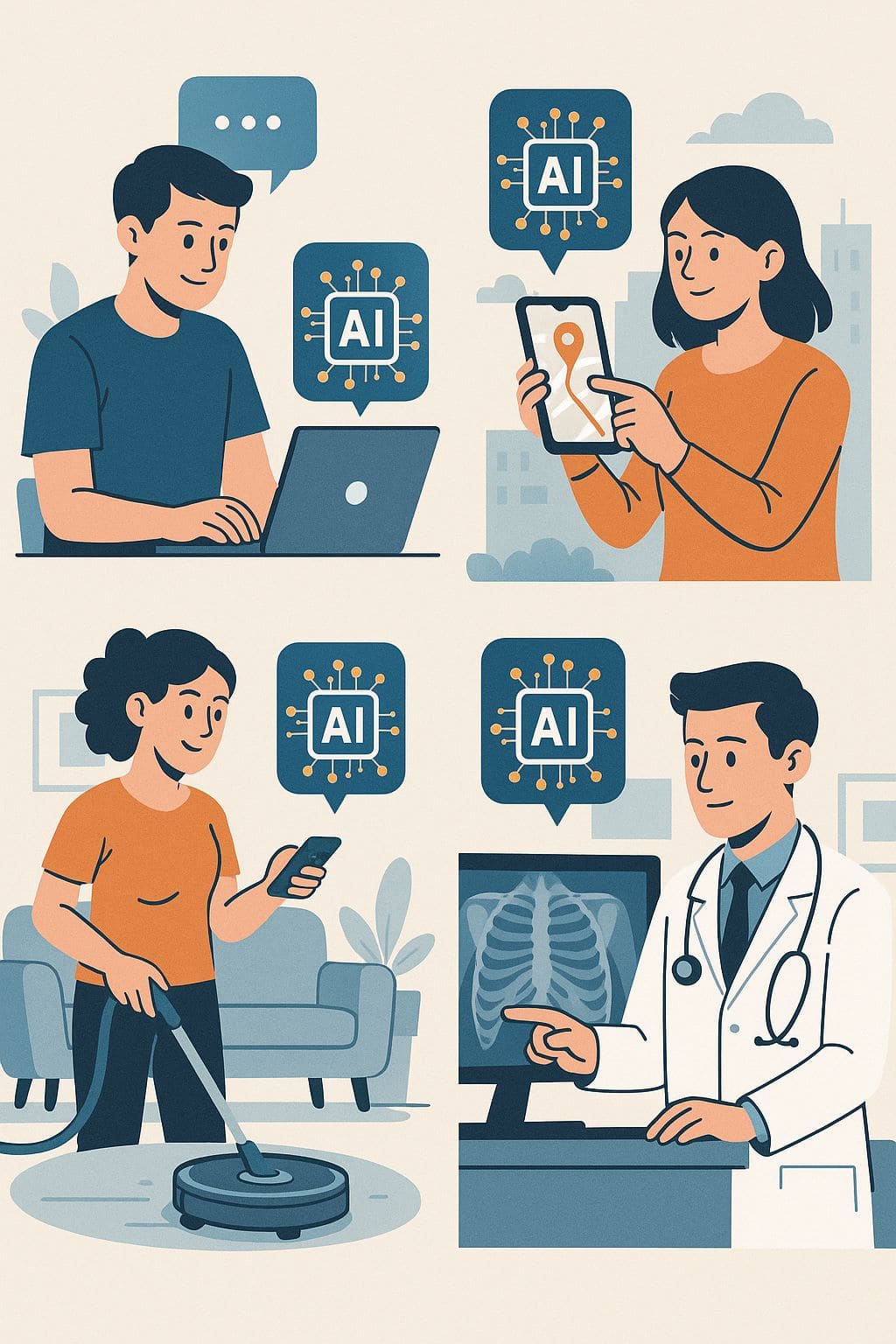

AI Applications by Industry
Healthcare Revolution
AI is revolutionizing healthcare through advanced diagnostic and treatment support systems.
- Diagnostic support: AI analyzes medical images (X-rays, MRIs) to detect diseases like early-stage cancer more accurately
- Virtual medical assistants: IBM Watson understands natural language and searches vast medical literature to suggest treatment plans
- Medical chatbots: Guide patients, schedule appointments, remind medication
- Drug discovery: AI accelerates the development of new medications
Business & Finance
Enterprises use AI to automate processes and gain competitive advantages.
- Process automation: Automate repetitive tasks, freeing human labor for creative work
- Predictive analytics: Machine learning algorithms predict business trends and understand customers better
- Fraud detection: Analyze unusual transaction behavior to prevent financial crimes
- Credit scoring: More accurate assessment of loan risks
- Automated trading: High-speed stock trading algorithms
- Customer support: 24/7 chatbots answering basic questions
Educational Innovation
AI offers great potential in education, from automatic grading to personalized learning support.
- Automatic grading: Grade multiple-choice tests and basic essays, reducing teachers' workload
- Personalized learning: Track individual student progress and suggest tailored study plans
- AI tutors: Interact with students, answer questions, and guide exercises
- Adaptive content: Adjust difficulty based on student performance
Transportation Evolution
The transportation sector benefits clearly from AI through autonomous vehicles and intelligent traffic management.
- Autonomous vehicles: Self-driving cars combine AI algorithms in vision, machine learning, and decision-making
- Traffic management: Analyze real-time traffic data, predict and coordinate traffic signals
- Route optimization: Reduce congestion and accidents through intelligent routing
- Fleet management: Optimize delivery scheduling and demand forecasting
Smart Agriculture
AI participates in smart agriculture through sensors and machine learning systems.
- Crop monitoring: Sensors and AI systems monitor plant health and growth
- Weather forecasting: Predict weather patterns for optimal farming decisions
- Resource optimization: Optimize irrigation and fertilization based on soil and climate data
- Automated harvesting: AI robots identify weeds and automate crop collection
Entertainment & Content Creation
AI plays a major role in personalizing experiences and creative content generation.
- Content recommendations: Music and video streaming services use AI to recommend content suited to individual tastes
- Creative AI: Produce music, create art, write scripts
- Dynamic content: Generate illustrations from text descriptions
- Interactive entertainment: Characters and storylines that dynamically respond to players
In summary, AI is present in almost every aspect of life. From small tasks like filtering spam emails, recommending songs, to major roles like supporting medical surgery and managing smart cities – AI quietly enhances efficiency and convenience for humans. Understanding AI's practical applications helps us better grasp the value AI brings and prepare for a future living and working alongside these "intelligent machine companions."
Benefits of AI for Life and Society
AI brings many significant benefits at both individual and organizational levels. Below are some key advantages of artificial intelligence:
Task Automation
Automate repetitive manual tasks, freeing human labor for creative work
- 24/7 production lines
- Automated data entry
- Email classification
Speed & Efficiency
Process data and compute much faster than humans
- Analyze millions of records in seconds
- Faster decision-making
- Reduced operational costs
Continuous Learning
AI systems become increasingly intelligent through experience
- Learn from new data
- Improve quality over time
- Adapt to user feedback
Personalization
Create products and services tailored to individuals
- Personalized recommendations
- Customized learning paths
- Enhanced user satisfaction
Big Data Analysis
Extract meaning from massive datasets and predict trends
- Discover hidden patterns
- Weather prediction
- Market forecasting
Improved Accuracy
More accurate and consistent than humans in rule-based tasks
- Medical image analysis
- Precision manufacturing
- Reduced human error
Thanks to these benefits, most industries today have implemented AI to some extent. AI helps increase productivity, reduce costs, and improve product and service quality. For individual users, AI brings a more convenient life: more personalized entertainment, better healthcare, safer transportation, and more. However, alongside benefits come challenges that require us to understand and use AI responsibly and effectively.

Challenges and Limitations of AI
Despite AI's great potential, its application raises many challenges and concerns. Below are some key issues:
High initial deployment costs: Building effective AI systems requires large investments in infrastructure (servers, specialized computing devices) and expert personnel for development and maintenance. Not all organizations can afford this. Additionally, data – the raw material for AI – must be collected and standardized, which takes time and money.
Integration demands on existing processes: To apply AI, businesses must change or adjust their workflows. Integrating new technology can cause initial disruption, requiring retraining staff and time to adapt. Without proper strategy, AI may interrupt business operations short-term.
Data and privacy issues: AI needs massive data, including personal data (user behavior, health info, facial images, voice). Collecting and processing this data raises privacy concerns.
Transparency and explainability: Many complex AI models (especially deep learning) operate as "black boxes" – it's hard to understand why they make certain decisions. This poses challenges in fields requiring clear decision explanations.
For example, if AI denies a loan application, banks need to explain the reason to customers, but AI algorithms may not provide understandable reasons. Lack of transparency also reduces user trust, especially in critical situations like medical diagnosis or autonomous driving.
Job displacement due to automation: AI automates many tasks, meaning some traditional jobs may be replaced. This raises concerns about unemployment for certain workers. Repetitive jobs (assembly lines, data entry, basic customer support) are at high risk.
Ethical and safety issues: This is the biggest social challenge. AI can be misused for malicious purposes: creating fake news (deepfakes) that spread misinformation, automated cyberattacks, lethal autonomous weapons, etc.
These risks demand urgent AI ethics: ensuring AI acts ethically, complies with laws, and respects human values. Experts also warn of existential risks if AI surpasses human control, a distant but not negligible scenario.
Dependence and loss of control: Over-reliance on AI may cause humans to lose some skills and intuition. For example, dependence on GPS can reduce navigation skills; reliance on AI recommendations may reduce independent thinking.
Moreover, if critical AI systems fail or are attacked, consequences can be severe (humans lose timely intervention ability due to delegation to AI). Therefore, maintaining human oversight is essential, especially while AI is not yet perfect.
| Challenge Category | Impact Level | Timeframe | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation Costs | High | Immediate | Gradual adoption, cloud solutions |
| Privacy Concerns | Critical | Ongoing | Regulation, data protection |
| Job Displacement | High | Medium-term | Retraining programs |
| Ethical Issues | Critical | Long-term | AI governance frameworks |
These challenges show that AI development and application require caution and responsibility. Organizations deploying AI must carefully consider legal and ethical aspects; national and international legal frameworks and AI management standards are needed. Users should also raise awareness to use technology safely. Artificial intelligence, no matter how smart, must be guided by humans – to ensure it serves society's common good.
The Future of AI – Trends and Prospects
There is no doubt that AI will continue to develop strongly and increasingly impact humanity's future. Based on current trends, we can imagine some main AI trends and prospects in the coming years:
Increasingly Intelligent AI
Universal Adoption
Creative AI Revolution
Ethical AI Focus
Key Future Trends
AI Becoming Increasingly Intelligent
AI models (especially Generative AI) will continue improving in understanding and content creation. New versions of large language models will be able to converse more naturally, even remember long-term context and have broader knowledge.
- Personal virtual assistants that truly listen, empathize, and support many aspects of life
- Digital companions for mental health care and stress reduction
- More natural human-AI interaction
- Enhanced contextual understanding
Universal AI Integration
While AI is currently a competitive advantage for some pioneering companies, in the near future AI will become a mandatory standard. Like electricity or the internet, AI will be integrated by default into products and services.
- Smart factories with AI managing optimal operations
- Smart farms using AI to monitor crops and livestock
- Smart cities with AI coordinating traffic, utilities, and security
- Workforce requiring AI operation knowledge
The Rise of Creative AI
AI will not only assist but also co-create with humans in many artistic and design fields. Increasingly, AI creative tools support artists in music, painting, filmmaking, writing faster or suggesting new ideas.
Music & Audio
AI composition and sound design
Visual Arts
AI-generated artwork and design
Film & Video
Dynamic storylines and characters
Gaming
Adaptive gameplay experiences
Focus on Ethical AI
Given AI's growing power, the world will pay special attention to building legal and ethical frameworks for AI. Governments and international organizations are discussing AI governance regulations.
- Ensure technology is used for good purposes without discrimination
- Respect privacy and safety standards
- Transparency, explainability, and accountability for AI errors
- AI certification standards before deployment
- Professional codes of conduct for AI developers
Moving Toward General AI (AGI)
Although AGI is still distant, major tech companies like OpenAI, DeepMind, Meta, etc., are diligently pursuing this path. Every advance in narrow AI is a stepping stone toward AGI.
Impact on Labor Market
In the near future, AI will change the nature of many jobs. Repetitive tasks will gradually be done by machines, but at the same time, AI workforce demand will explode.
Automated Tasks
- Assembly line work
- Data entry
- Basic customer support
- Routine analysis
Emerging Roles
- Algorithm developers
- Data engineers
- AI analysts
- AI trainers & auditors

In summary, the future of AI offers both great opportunities and significant challenges. This technology promises to help humanity achieve unprecedented achievements and solve complex problems (climate change, pandemics, poverty) through artificial intelligence power.
At the same time, it forces us to seriously consider responsibility and ethics when empowering machines. The path ahead for AI will be shaped by human choices today. With wisdom and global cooperation, we can harness AI to create a bright future where humans and artificial intelligence coexist and thrive together.
Conclusion
AI (artificial intelligence) is no longer a distant concept from science fiction but has become an essential part of modern life. By simulating human intelligence, AI helps machines perform many tasks from simple to complex – from answering everyday questions to driving, big data analysis, and supporting important decisions.
Useful Applications
AI has many useful applications across various fields, bringing great benefits in efficiency, accuracy, and personalized experiences
Real Challenges
AI poses technical, economic, and ethical challenges that we must jointly address
Responsible Use
Every technology has two sides; what matters is humans use it with intelligence and responsibility
In the future, AI is expected to develop even more strongly, becoming smarter and closer to humans. Artificial intelligence will surely play a central role in the digital transformation and scientific progress of the 21st century. Understanding AI correctly from now on will help each of us be ready to embrace the changes AI brings and know how to apply AI effectively and safely in learning, work, and life.
AI is the key that opens the door to the future. With knowledge, preparation, and proper direction, we can turn artificial intelligence into a powerful ally, conquering new heights together for a better life for all. AI is humanity's creation – and ultimately, it should serve humans according to the best goals. That is the core when understanding AI.






