AI in Customer Care
AI in Customer Care is revolutionizing customer service by enabling faster responses, personalized support, and 24/7 availability. With chatbots, automation, and predictive insights, businesses can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and boost customer satisfaction.
AI-driven customer support uses tools like chatbots, virtual assistants, and machine learning to handle routine inquiries and personalize service. These systems interpret customer queries and leverage data—purchase history, past tickets, FAQs—to automate answers or escalate complex issues to humans.
By automating repetitive tasks and drawing insights from customer data, AI makes support faster and more consistent, allowing companies to offer 24/7 assistance without overloading agents.
The result is a smoother, more efficient service experience where customers get instant help, and human teams are freed to focus on sensitive or high-value issues.
Why AI is Transforming Customer Care
Businesses face rising expectations for fast, personalized support. A Salesforce survey found that 82% of service professionals report customer demands have grown, and 78% of customers feel service is too slow or rushed. AI helps bridge that gap by providing real-time, personalized assistance that transforms service into a strategic advantage.
Higher Satisfaction
Faster Resolution
Cost Reduction
For example, generative AI can analyze a customer's history and offer tailored recommendations or proactively resolve issues even before a call is made. Companies that mature in AI adoption see measurable gains across multiple dimensions.
Key Benefits of AI-Powered Support
24/7 Instant Support
Chatbots and virtual assistants never sleep, answering common questions at any hour and greatly reducing wait times.
- Always-on availability
- 40% increase in customer engagement
- Zero wait times for routine queries
Faster Response Times
AI agents reply instantly to simple inquiries and suggest answers for agents on tougher questions, dramatically cutting hold times.
- Instant automated responses
- Real-time agent assistance
- Proactive customer-driving function
Cost Efficiency
Automating routine tasks reduces staffing needs for basic inquiries, with chatbots saving up to 30% of service expenses.
- 30% current cost savings
- Resource reallocation to high-value activities
- Reduced operational overhead
Empowered Agents
AI handles tedious work, freeing human agents for complex or sensitive issues while boosting their productivity.
- 14% average productivity increase
- Real-time response suggestions
- Sentiment alerts and guidance
Personalization
AI analyzes customer data and behavior to deliver tailored suggestions and solutions matching individual history.
- 10× faster personalized recommendations
- 15% satisfaction lift
- 81% of customers expect personal touch
Data-Driven Insights
AI collects and examines vast interaction data, yielding deeper customer insights for product and service improvements.
- Trend and pain point identification
- Churn prediction capabilities
- Proactive issue detection

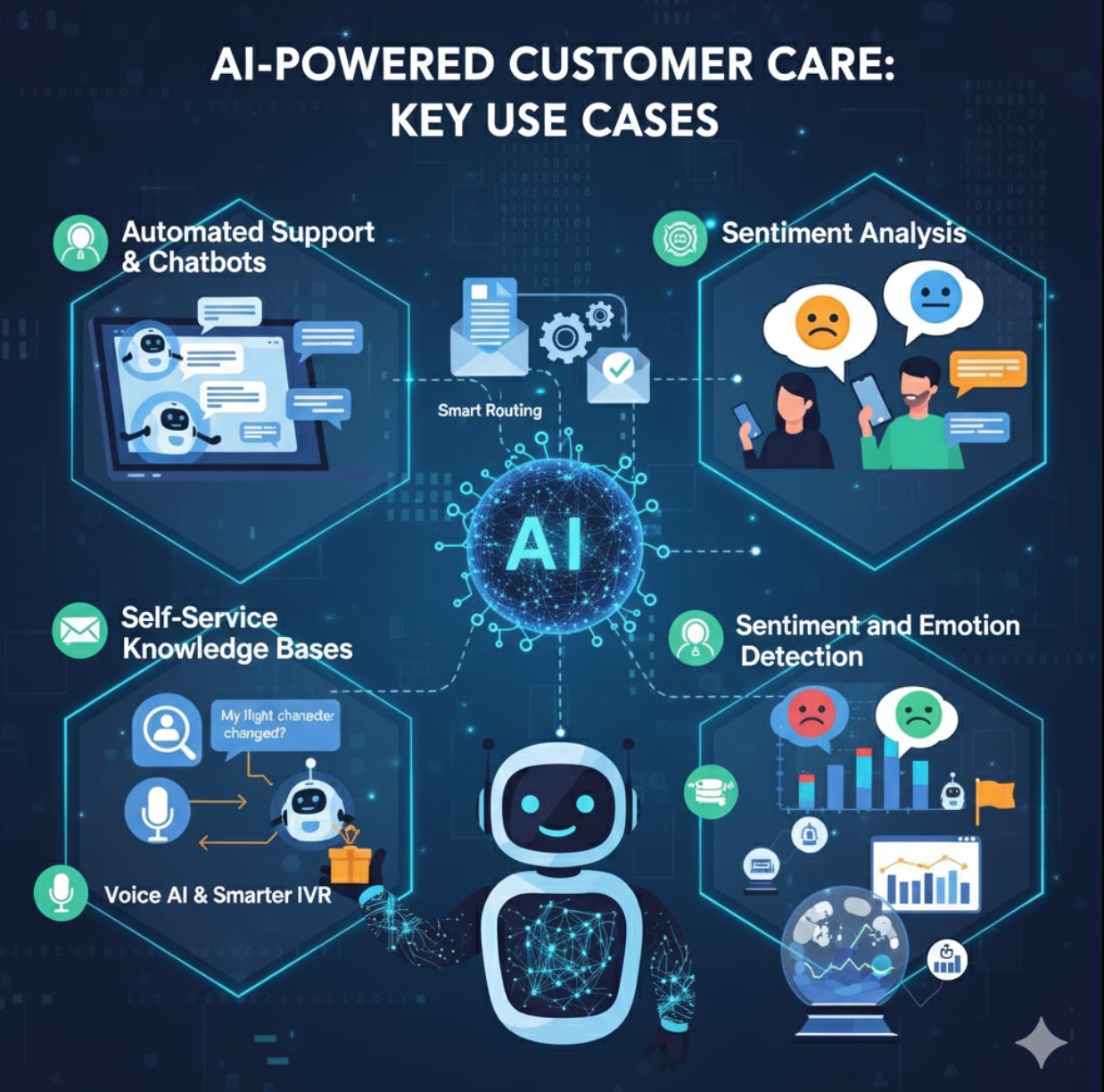
AI-Powered Customer Care: Key Use Cases
AI has a wide array of applications in customer support. Companies across industries are already using these tools in practice—for example, many e-commerce and travel firms deploy chatbots to handle common queries about orders or bookings, instantly answering questions about flight changes or return policies and reducing the workload on human agents.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
Self-Service Knowledge Bases
Intelligent Ticket Routing
Voice AI and Smarter IVR
Sentiment and Emotion Detection
Predictive and Proactive Support
Workflow Automation
The mix of chatbots, analytics and automation means routine issues are solved instantly, while complex problems get routed to humans with all the right context.
Implementing AI in Customer Care
Successfully adding AI to support requires planning and best practices. Following strategic implementation guidelines ensures you maximize benefits while avoiding common pitfalls.
Define Clear Objectives
Start by identifying specific goals (e.g. "reduce average wait time by 50%" or "increase self-service rate"). This ensures you select AI tools aligned to measurable outcomes rather than just experimenting aimlessly.
Keep the Human Touch
AI should augment, not replace humans. Best use cases are routine inquiries and data-heavy tasks. Design workflows so that emotional or complex cases always have a clear path to a live agent.
Be Transparent
Let customers know when they're interacting with AI. Transparency builds trust—if users see an AI chatbot, they'll know what to expect. Ensure AI's use complies with privacy laws (GDPR, CCPA, etc.) and company policies.
Train on High-Quality Data
AI models are only as good as the data they learn from. Populate your AI systems with clean, accurate, and up-to-date knowledge (product info, scripts, FAQs). Regularly review and update this knowledge base to prevent outdated or biased responses.
Continuous Improvement
Monitor performance and gather feedback. Use analytics on KPIs like resolution rate and customer satisfaction to see how AI is doing. AI deployment isn't "set and forget"—it improves with iteration.
Seamless Integration
Choose AI solutions that plug into your existing support platforms (CRM, ticketing system, live chat, etc.). This way, agents retain full context in one interface, and customers get a unified experience.
Personalize Interactions
Use the customer data you already have. Ensure AI makes use of past order history or preferences to tailor answers. Customers notice when AI mentions details like their name or product owned—this personalization increases satisfaction.
Ethical and Responsible Use
Consider fairness and privacy. Avoid using sensitive personal attributes as targeting criteria. Audit AI outputs to catch any biased or inappropriate suggestions. Follow privacy best practices so customer data is protected.
Train Your Team
Prepare your staff. Train agents and managers on how the AI works and when to override it. Show employees that AI is a tool to help them do their jobs better (not a threat), and involve them in the rollout.
By following these strategies—clear goals, good data, transparency and human oversight—businesses can smoothly integrate AI into customer care and maximize its benefits.

Challenges and Considerations
While powerful, AI also brings challenges that organizations must carefully address. Understanding these concerns and implementing appropriate safeguards is essential for successful AI adoption.
Trust & Privacy
Many customers worry about AI mishandling their data. Only about 42% trust companies to use AI ethically. To build confidence, be clear about data use and comply with regulations.
- Transparent data usage policies
- Regulatory compliance (GDPR, CCPA)
- Visible controls (option to talk to a human)
- Clear communication about AI interactions
Accuracy and Bias
AI models can "hallucinate" or give incorrect answers, especially if trained on poor-quality data. Erroneous or biased responses can frustrate customers or even cause legal issues.
- Regular review and testing of AI outputs
- Human-in-the-loop checks
- Continuous monitoring systems
- Quality assurance protocols
Maintaining Empathy
Over-automation risks losing the human touch. Not every interaction fits an algorithm. Companies should ensure that difficult or emotional cases can quickly be forwarded to empathetic human agents.
Skill Gaps
Implementing and managing AI systems requires new expertise. Many teams lack trained personnel, requiring investment in training or hiring AI specialists.
- Comprehensive training programs
- AI literacy culture development
- Hiring specialized AI personnel
- Ongoing education initiatives
Integration Complexity
Adding AI can be technically complex. Many companies start with pilot projects (e.g. a single chatbot for one product line) and expand gradually.
Ethical and Legal Issues
Data used to train AI must be handled responsibly. Laws like GDPR require consent and transparency. Companies should assess ethical implications and have safeguards against misuse.
- Consent and transparency requirements
- Ethical impact assessments
- Safeguards against manipulation
- Clear governance policies
By anticipating these challenges, customer care leaders can mitigate risks. In practice, pairing AI with human oversight and maintaining clear policies usually solves most issues. While AI offers many upsides, concerns about job impacts and data privacy must be carefully managed through communication and training.

The Future of AI in Customer Care
AI's role in customer service is only accelerating. Industry experts predict bold changes ahead that will fundamentally reshape how companies interact with customers.
Agentic AI
Cost Reduction
Universal Adoption
Soon 100% of customer interactions will involve AI in some form.
— Zendesk CEO
Emerging Technologies
Advanced Language Models
Large language models (like GPT-4 and beyond) and advanced voice assistants will make interactions more conversational and "human-like".
Multilingual AI
Breaking down language and accessibility barriers with real-time translation and localization capabilities.
Emotion AI
Advanced sentiment analysis and emotional intelligence for more empathetic automated interactions.
Customer-Side AI
Customers using their own AI tools to engage companies, challenging traditional support models.
The Hybrid Model
Experts emphasize that AI will enhance but not replace humans. As one report puts it, "AI is a game-changer for customer service," but success lies in combining AI's speed with human empathy.
Traditional Support
- Reactive problem-solving
- Limited personalization
- Business hours constraints
- Manual ticket routing
- Generic responses
AI-Enhanced Support
- Proactive issue prevention
- Hyper-personalized service
- 24/7 intelligent assistance
- Automated expert routing
- Context-aware interactions
In summary, AI is set to revolutionize customer care. Companies that master this technology—while keeping trust, privacy and human connection in check—will deliver the responsive, personalized support that tomorrow's customers will demand.

Top AI Customer Service Tools
Zendesk
Application Information
| Author / Developer | Zendesk, Inc. (founded by Mikkel Svane, Alexander Aghassipour, Morten Primdahl) |
| Supported Devices | Web browsers (desktop, mobile), iOS and Android apps (Zendesk Support app) |
| Languages / Countries | Multi-language support with localization across all products (Support, Guide, Chat, and more) |
| Pricing Model | Paid plans starting from $19 per agent/month (free trial available, no permanent free plan) |
General Overview
Zendesk is a leading cloud-based customer service platform that centralizes customer interactions from email, chat, phone, social media, and web forms into a unified ticketing system.
It provides tools for automation, self-service, reporting, and customization to enable organizations to scale support operations while maintaining consistency and responsiveness. Zendesk also supports rich developer extensibility via APIs, embeddables, and a marketplace of apps.
SEO Benefits & Digital Presence
In the modern digital era, strong customer support presence also influences SEO and brand reputation.
Zendesk's knowledge base and help center (Zendesk Guide) allows businesses to publish optimized help articles and FAQs, which can be indexed by search engines, thereby driving organic traffic to support content. Its SEO-friendly URLs, structured content, and internal linking strategies can improve search visibility.
Moreover, integration of Zendesk embeddables and web widget allows on-site support without redirecting users off your domain, which helps retention and reduces bounce. From an SEO perspective, having a robust, searchable help center powered by Zendesk can contribute to better user experience, longer dwell time, and keyword relevance in support-related queries.
Key Features
Unified inbox consolidating email, chat, voice, messaging, and social media interactions
Zendesk Guide for help centers, FAQs, and community forums with SEO optimization
Triggers, macros, SLA management, and intelligent workflow automation
APIs, SDKs, embeddables, and marketplace apps for custom integrations
Dashboards, reporting tools, and Explore analytics for data-driven insights
Bot agents, intelligent suggestions, and copilot features for enhanced support
Native iOS and Android apps for agents to respond on the go
Localization across workflows, dynamic content, and translations
Download or Access Link
User Guide
Start with a trial, define your subdomain (e.g. yourcompany.zendesk.com).
Enable email, chat, social, voice as desired in Admin settings.
Use triggers, macros, and SLAs to route and automate ticket assignments.
Use Zendesk Guide to publish support articles, FAQs, and organize content.
In Admin > Localization, add additional languages and translate Help Center content.
Download iOS / Android app and log in with agent credentials.
For in-app support, embed Zendesk's Web Widget or mobile SDK to allow users to open tickets without leaving your site/app.
Use built-in dashboards or Zendesk Explore for deeper insights.
Access the API to integrate with CRMs or build custom apps via the Zendesk Apps Framework (ZAF).
Notes & Limitations
- No permanent free plan available (only free trials offered)
- Advanced features (AI, multilingual support, custom roles, sandbox) require higher-tier plans or paid add-ons
- Complex setup process for customizing workflows, integrations, and translations may require technical expertise
- Per-agent pricing and add-ons can escalate costs substantially as you scale
- Language support varies by product; not all Zendesk products support every language
- Mobile app limitations include occasional link-opening issues, missing macro functionality, and push notification inconsistencies
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes — Zendesk provides a Web Widget and mobile SDKs so users can open tickets or chat without leaving your app or site.
Yes — you can configure multiple languages for Support, Guide, Chat, etc., and use dynamic content or translation workflows.
For the Support product, pricing starts around US $19 per agent/month (entry plan).
Yes — Zendesk offers extensive REST APIs (ticketing, help center, live chat, voice, custom objects) and an Apps framework (ZAF) for building integrations.
No — AI, bot agents, copilot, and intelligent automation are offered as add-ons or part of higher-tier plans.
Freshdesk
Application Information
| Author / Developer | Freshworks Inc., originally launched as Freshdesk by founders Girish Mathrubootham and Shan Krishnasamy |
| Supported Devices | Web browsers (desktop and mobile), native mobile apps on Android and iOS |
| Languages / Countries | Supports multilingual capabilities (30+ languages) for help portal, notifications, widget, and AI bots (Freddy); available globally and used across many countries |
| Pricing Model | Offers a free plan (up to 2 agents) with basic features; paid plans start from ~$15/agent/month (annual billing) for more advanced support tiers |
General Overview
Freshdesk is a cloud-based customer support and helpdesk platform that enables organizations to centralize customer communications from email, chat, phone, social media, and web widgets into one unified ticketing system. It focuses on ease of use, automation, AI assistance, and scalability for teams of all sizes. With integrations, mobile access, and a multilingual help center, Freshdesk helps businesses streamline their support operations and deliver faster, more consistent customer service.
SEO Benefits and Capabilities
From an SEO perspective, Freshdesk's help center (knowledge base) offers a powerful way to publish support content that is indexable by search engines, driving organic traffic to answers for common customer questions.
By organizing topics, FAQs, and articles with SEO-friendly URL structures and metadata, Freshdesk helps companies boost visibility for user queries. Coupled with internal linking, structured content components, and multilingual support, Freshdesk's knowledge base can become a content asset that not only aids customers but also enhances domain authority.
Embedding Freshdesk's widget on your website allows users to get support without leaving your domain, reducing bounce and improving dwell time, which are positive signals for SEO.
Key Features
Unify queries from email, web, chat, social, phone into a single inbox for streamlined support management.
Build comprehensive help portals, self-service resources, and community forums to empower customers.
Automate repetitive tasks with triggers, routing, SLAs, and macros to boost agent productivity.
Leverage Freddy AI Agent, Copilot, and Insights for intelligent automation and data-driven decisions.
Manage tickets on the go with native Android and iOS apps featuring push notifications.
Deliver support in 30+ languages across help portals, widgets, bot interactions, and translations.
Connect with hundreds of apps and extend functionality through robust API support.
Access prebuilt and custom reports with comprehensive dashboards to track performance metrics.
Download or Access Link
User Guide
Register for a Freshdesk account, choose your subdomain, and configure basic settings to get started.
Define agent roles, permissions, and assign agents to teams for organized support operations.
Integrate email, web widget, chat, social media, and phone (via Freshcaller or BYOT) into the ticketing system.
Create triggers, automation rules, SLA policies, macros, and ticket routing to streamline operations.
Use the Guide/Help Center to publish articles, FAQs, categorize content, and enable multilingual versions.
Activate Freddy AI features to auto-respond, suggest articles, or assist agents, depending on your plan.
Agents can install the Freshdesk mobile app (iOS/Android) to respond to tickets on the go.
In Admin > Helpdesk Settings > Manage Languages, add languages and translate notifications, ticket fields, and portal content.
Monitor metrics, build custom reports, and track performance trends to optimize support operations.
Use the Freshdesk Marketplace or APIs to integrate CRM, e-commerce, chat tools, and extend functionality.
Notes & Limitations
- Free plan is limited to 2 agents and only basic features
- Many advanced capabilities (AI, advanced automation, multilingual support) require higher-tier or add-on plans
- Mobile apps may not support full feature set compared to web version
- Steeper learning curve when configuring complex workflows, automation, and large team management
- Costs scale with number of agents and add-on features, which may become expensive for growing teams
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, Freshdesk offers a free plan for up to 2 agents with basic ticketing, knowledge base, and reporting features.
Freshdesk supports over 30 languages for portals, notifications, and bots. Freddy AI supports many languages as well, including Arabic, Korean, Spanish, Vietnamese, and more.
AI features (Freddy AI Agent, Copilot, Insights) are included in certain higher tiers or as add-ons, not in the base free or lower plans.
Yes — via Freshcaller (Freshworks' telephony solution) or BYOT (Bring Your Own Telephony), integrating voice into the ticket system.
Yes — through the Manage Languages settings, you can add and translate portal content, ticket fields, and knowledge base articles.
Intercom
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Developer | Intercom, Inc. |
| Platform Support | Web-based, Android, iOS |
| Languages | English, French, German, Spanish, and more (available globally) |
| Pricing Model | Paid plans with free trial No Free Plan |
What is Intercom?
Intercom is a leading conversational relationship platform that enables businesses to communicate with customers through messaging, chatbots, and automation tools. Designed to enhance customer support, engagement, and retention, Intercom combines live chat, AI-powered bots, and integrated helpdesk tools into a single solution.
The platform is trusted by global brands to deliver personalized, real-time interactions across websites, mobile apps, and emails. With a focus on seamless customer experience, Intercom empowers teams to scale support while maintaining a personal touch.
Why Intercom Matters for Your Business
Intercom plays a vital role in modern digital marketing and customer relationship management, particularly within SEO and customer engagement strategies. By providing real-time communication tools, it helps businesses reduce bounce rates, increase conversions, and enhance user satisfaction—key factors for SEO performance.
The AI chatbot "Fin" automates repetitive queries, while proactive messaging nurtures leads and keeps visitors engaged. Its integration with CRM systems, analytics tools, and marketing platforms ensures that businesses can analyze user behavior and optimize touchpoints for better retention and search visibility.
Whether for SaaS startups or enterprise-level companies, Intercom offers a unified solution for managing conversations and improving customer journeys that ultimately boost online presence and brand trust.
Key Features & Capabilities
Advanced chatbot "Fin" handles automated support and response management, reducing team workload while maintaining quality.
Manage multi-channel conversations efficiently from a single dashboard with smart categorization and assignment.
Deliver personalized in-app and email messages to engage customers at the right moment in their journey.
Build automated workflows and processes tailored to your support team's specific needs and requirements.
Track performance metrics, response times, and engagement data with comprehensive reporting tools.
Connect with CRM, email platforms, and analytics tools including Salesforce, HubSpot, and Google Analytics.
Download or Access Intercom
Getting Started with Intercom
Create your Intercom account and integrate the widget into your website or mobile app using the provided code snippet.
Adjust design elements, language preferences, and visibility settings to match your brand identity and user experience goals.
Set up AI bots and message triggers to respond to frequently asked questions and guide users through common workflows in real-time.
Use the inbox dashboard to categorize, assign, and resolve customer messages efficiently with your support team.
Track chat performance, response times, and engagement metrics through built-in reporting tools to optimize your customer support strategy.
Important Limitations to Consider
- Premium features like AI automation and advanced workflows require higher-tier paid plans
- Mobile apps provide limited functionality compared to the full desktop experience
- Some setup and customization steps may require technical knowledge or developer assistance
- Pricing structure can become expensive for growing teams with high message volumes
Frequently Asked Questions
No, Intercom offers only a free trial period. All plans are paid subscriptions after the trial expires. There is no permanent free version available.
Yes, Intercom integrates seamlessly with popular tools including Salesforce, HubSpot, Slack, Google Analytics, and many other CRM, marketing, and analytics platforms.
"Fin" is Intercom's advanced AI-powered chatbot designed to provide instant, automated responses to customer queries and significantly reduce support team workloads while maintaining quality interactions.
Yes, Intercom offers scalable plans that can work for small businesses. However, smaller companies should carefully evaluate pricing based on their expected usage and feature requirements to ensure cost-effectiveness.
Intercom can be accessed on desktop computers, web browsers, and through dedicated Android and iOS mobile applications, providing flexibility for teams working across different devices.
Ada
Application Information
| Author / Developer | Ada Support, Inc. |
| Supported Devices | Web-based platform; accessible on desktop and mobile browsers |
| Languages / Countries | Supports over 50 languages and serves businesses globally |
| Pricing Model | Paid platform with custom pricing; no permanent free plan |
General Overview
Ada is an AI-driven customer service automation platform designed to streamline support and enhance customer engagement through intelligent chatbots and voice assistants. Founded in 2016, Ada empowers enterprises to deliver instant, personalized, and scalable customer interactions across messaging, email, and voice channels.
With advanced AI and generative technology, Ada helps businesses reduce operational costs, improve resolution times, and ensure 24/7 availability. Companies like Zoom, Shopify, and Verizon use Ada to automate customer conversations and provide a seamless omnichannel experience without compromising quality or consistency.
Detailed Introduction
Ada stands at the forefront of AI-powered customer experience (CX) transformation. Its platform enables businesses to automate up to 80% of customer inquiries using a blend of natural language understanding (NLU) and generative AI.
In the field of SEO and digital marketing, Ada helps brands maintain high customer satisfaction and engagement—key metrics that influence visibility and brand reputation online. By integrating with CRM systems, helpdesks, and analytics tools, Ada allows marketers and support teams to extract valuable insights from conversations.
These insights help improve keyword targeting, identify content gaps, and refine SEO strategies based on real user intent. Ada's multilingual support and omnichannel automation make it ideal for global businesses seeking to optimize user journeys and conversion funnels.
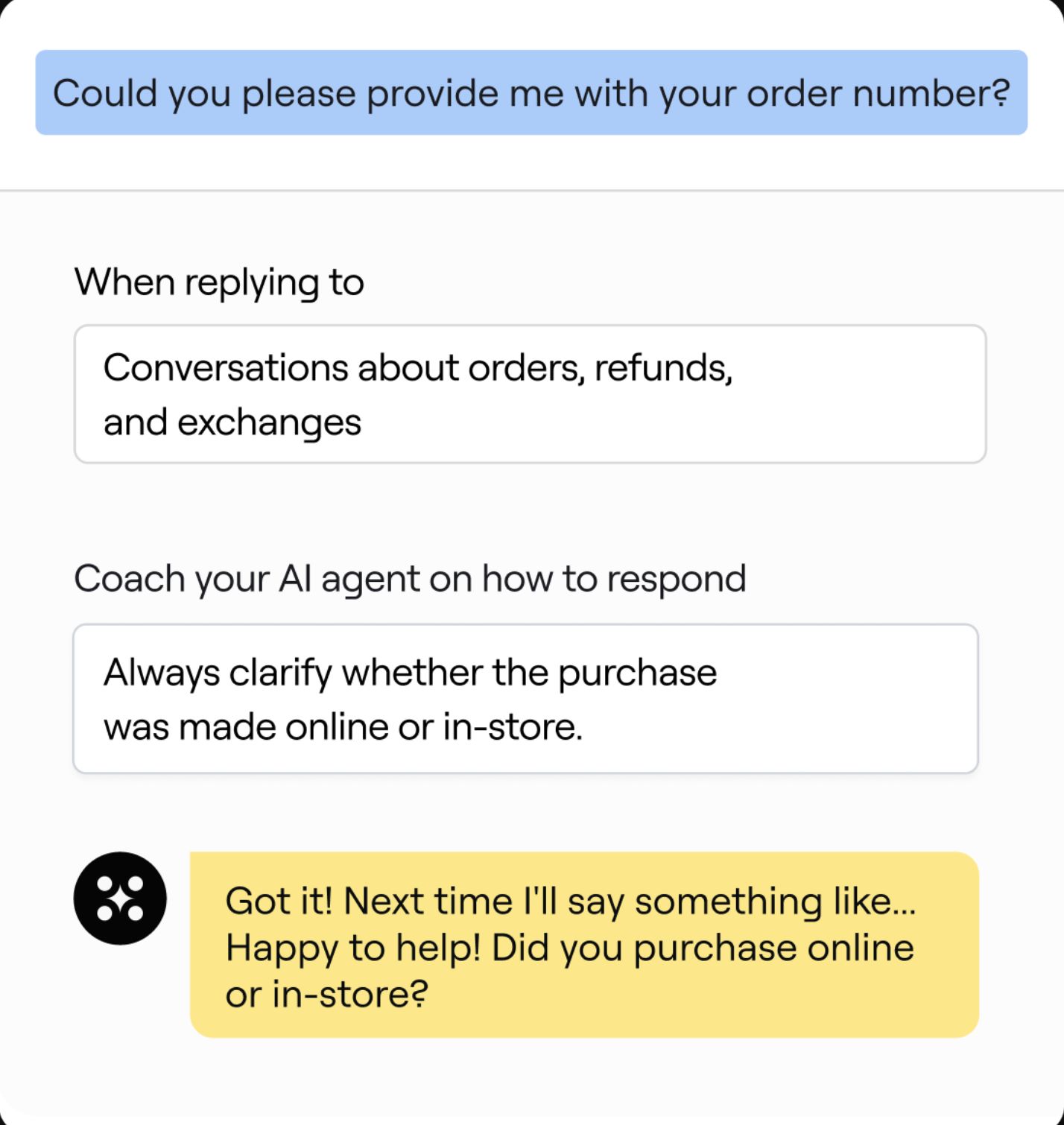
Key Features
Intelligent bots resolve repetitive customer queries using NLU and generative AI.
Manage customer interactions across chat, email, social media, and voice channels.
Seamlessly connect with CRMs, helpdesk systems, and knowledge bases.
Automate conversations in over 50 languages for global audiences.
Access detailed performance insights and optimization recommendations.
Download or Access Link
User Guide
Create an account on Ada's official website and define your business use cases.
Connect Ada with your existing CRM, ticketing systems, and knowledge base.
Use Ada's drag-and-drop interface or generative AI to train and design conversation flows.
Utilize Ada's test environments and analytics to refine responses.
Launch across web, mobile, or messaging platforms and monitor performance via the dashboard.
Notes & Limitations
- No free plan is available; pricing is based on business size and interaction volume.
- Setup and AI training may require technical expertise for optimal performance.
- Advanced analytics and integrations are available only on higher-tier plans.
- The platform relies heavily on the quality of the knowledge base content for accurate automation.
- Some features, like voice automation, may be limited depending on the selected plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ada is used to automate customer service and engagement through AI-driven chatbots and voice assistants.
Ada provides customized demos and consultations but does not have a public free trial or free plan.
Yes, Ada integrates with major CRM, marketing, and support systems, including Salesforce, Zendesk, and Intercom.
While primarily built for mid-sized and enterprise-level organizations, small businesses can use Ada depending on their automation needs and budget.
Ada supports over 50 languages, enabling global communication and multilingual customer service automation.
Key Takeaways
AI is transforming customer care by automating the routine and enriching the customer experience. Smart chatbots and virtual agents provide instant answers and round-the-clock service, boosting efficiency and satisfaction.
Balance is Key
Empowered Teams
Superior Outcomes
As industry research shows, organizations that combine AI speed with human emotional intelligence create superior service outcomes. Going forward, AI in customer care will only grow smarter and more pervasive—but by integrating it thoughtfully, businesses can delight customers, support agents, and the bottom line alike.







No comments yet. Be the first to comment!